Figure 2.
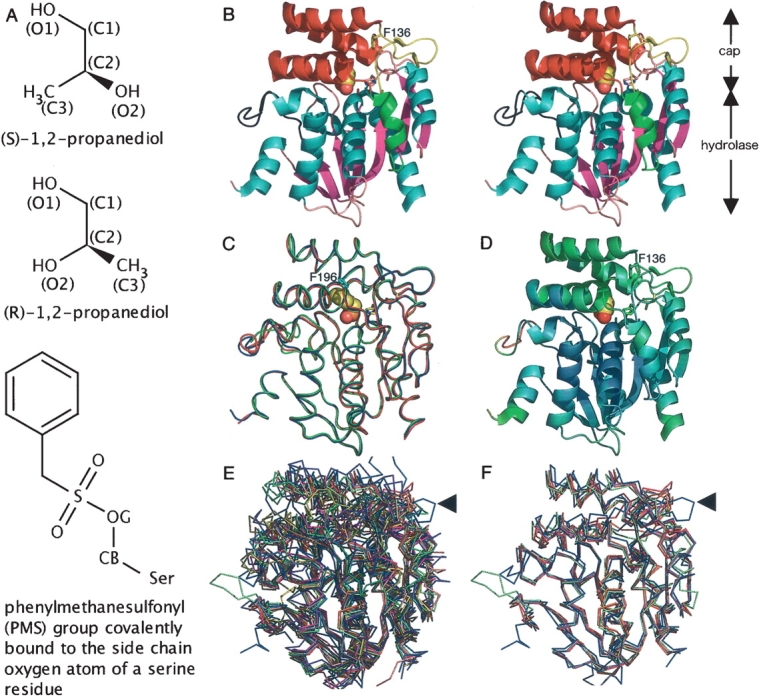
Overall structure and structural comparison with other α/β hydrolases. (A) Chemical structures of propylene glycol isomers and a phenylmethanesulfonyl (PMS) group covalently bound to the serine Oγ atom (denoted as OG). (B) Stereo side view of the native RsbQ (chain A). The propylene glycol molecule at the active site is shown in sphere representation. (C) Comparison of a native RsbQ molecule (chain A, blue) with the other molecule in the asymmetric unit (chain B, red) as well as with a PMS-bound molecule (chain A, green). The PMS group is shown in sphere representation. Phe196 is shown in cyan. (D) Ribbon representation of the native chain A molecule colored according to the temperature factors from blue (low) to red (high). (E) Twelve superposed structures. RsbQ is shown in blue. The unique loop region of RsbQ is indicated with an arrow. (F) RsbQ superposed with four cofactor-free haloperoxidases. Color usage is same as that in E.
