Figure 1.
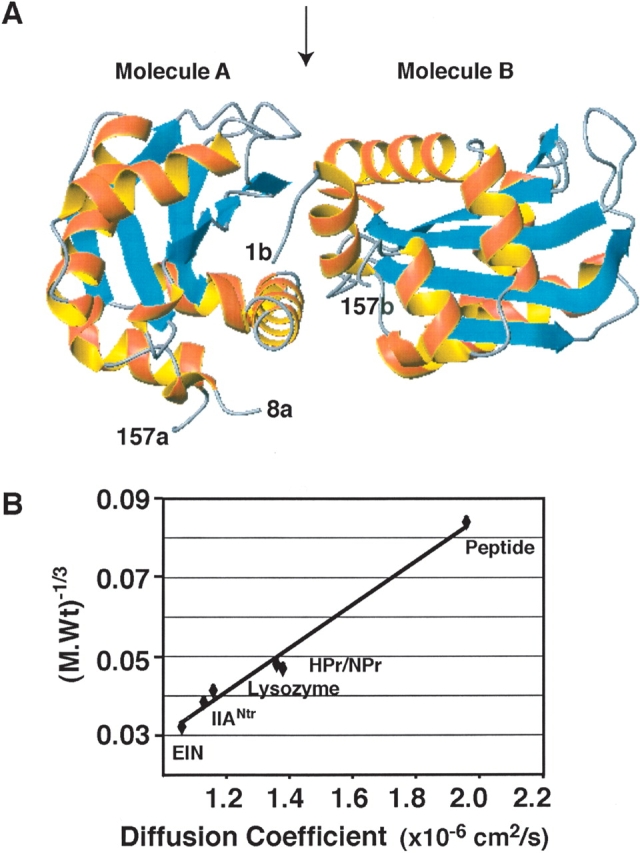
IIANtr is a dimer in the crystal but a monomer in solution. (A) In the crystal structure (PDB code: 1A6J), the coordinates for molecule A cover residues 8–157 (labeled 8a and 157a), while the coordinates for molecule B include residues 1–157 (labeled 1b and 157b). In both molecules, α-helices are in red and β-strands are in cyan. The interface between molecules A and B is indicated by an arrow at the top of the ribbon view of the structure (Bordo et al. 1998). This figure was made using MOLMOL (Koradi et al. 1996). (B) The molecular weight and diffusion coefficient of the proteins used in this study are a 15-residue peptide (1.7 kDa, 1.96 × 10−6 cm/sec) corresponding to the N-terminal amphitropic domain of the E. coli enzyme IIAGlc (Wang et al. 2003); HPr (~9 kDa, 1.36 × 10−6 cm/sec) (Garrett et al. 1999); NPr (with a C-terminal five-residue extension, ~10.2 kDa, 1.38 × 10−6 cm/sec); lysozyme (14.4 kDa, 1.16 × 10−6 cm/sec); IIANtr (~18 kDa, 1.13 × 10−6 cm/sec); and the N-terminal domain of enzyme I (EIN) (~30 kDa, 1.06 × 10−6 cm/sec) from E. coli (Garrett et al. 1999). A linear correlation was found between the cubic root of molecular weight and diffusion coefficient of these proteins with a correlation coefficient of 0.98.
