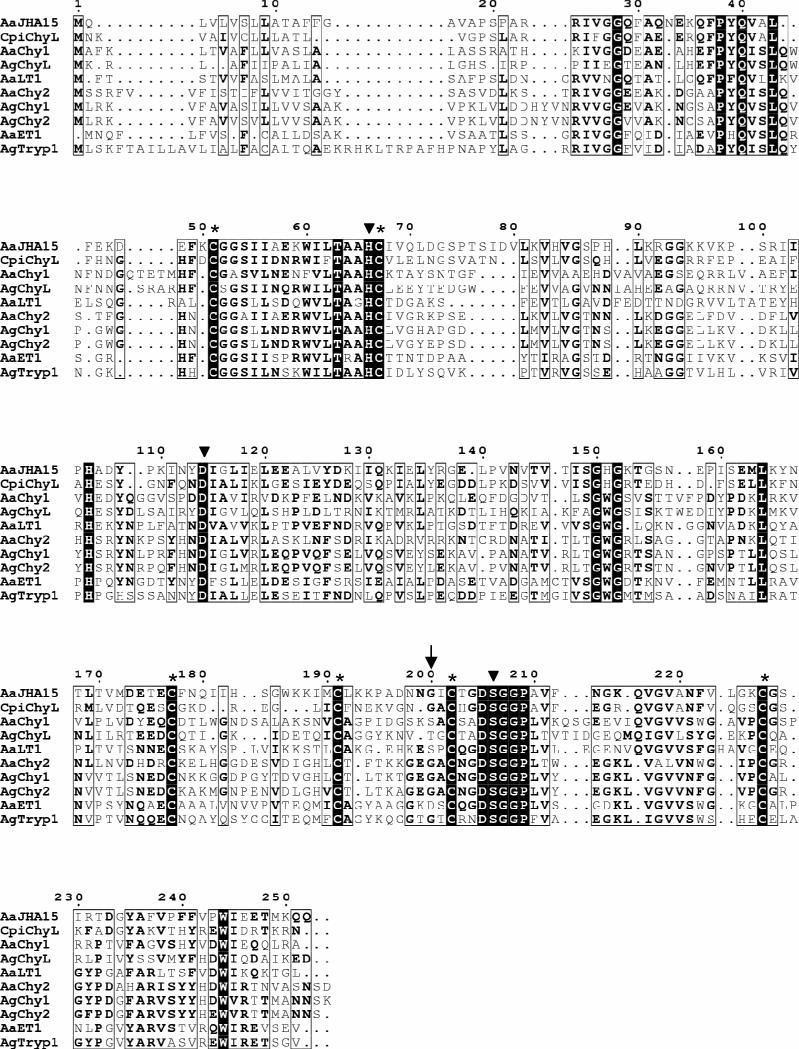
Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of the deduced Aedes aegypti JHA15 with other insect serine proteases. The sequences listed were retrieved from GenBank and the alignment was performed using MultAlin (http://bioinfo.genopoletoulouse.prd.fr/multalin/multalin.html). Solid triangles (▼) mark the active site residues of the catalytic triad (His/Asp/Ser), and the Gly residue characteristic of chymotrypsin-like serine proteases is indicated by an arrow (↓). Six conserved cysteines corresponding to the sites of the predicted disulfide bridges are denoted by asterisks (*). AaJHA15, Ae. aegypti chymotrypsin-like serine protease, AAX56968; CpiChyL, Culex pipiens chymotrypsin-like serine protease, AY958427; AaChy1, Ae. aegypti chymotrypsin 1, AAB01218; AgChyL, Anopheles gambiae chymotrypsin-like serine protease, AAC02700; AaLT1, Ae. aegypti late trypsin, AAA29356; AaChy2, Ae. aegypti chymotrypsin II-like protein, AAF43707; AgChy1, An. gambiae chymotrypsin-like protease ANCHYM1, CAA83568; AgChy2, An. gambiae chymotrypsin-like protease ANCHYM2, CAA83567; AaET1, Ae. aegypti early trypsin, 2211307A; AgTryp1, An. gambiae trypsin 1, CAA80513.