Fig. (2). Pathways of caspase activation during Alzheimer's disease.
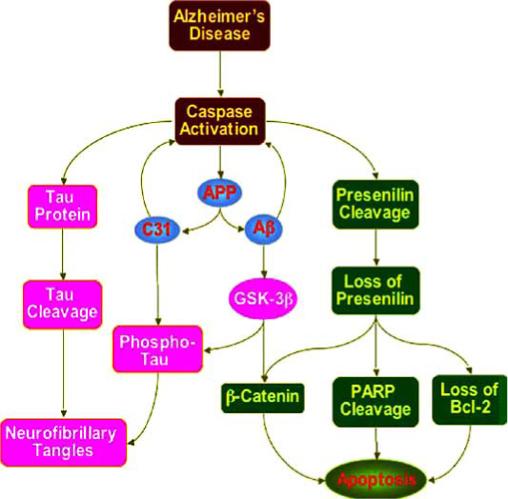
Caspase activation during Alzheimer's disease results in the cleavage of presenilin leading to apoptosis with loss of β-catenin, poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP), and Bcl-2. Caspases can cleave amyloid precursor protein (APP) and the resulting C-terminal fragment C31 resulting in hyperphosphorylation of tau protein (p-tau) as well as activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β). C31 and β-amyloid (Aβ) promotes the activation of caspases. Caspases also directly cleave tau protein to contribute to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles.
