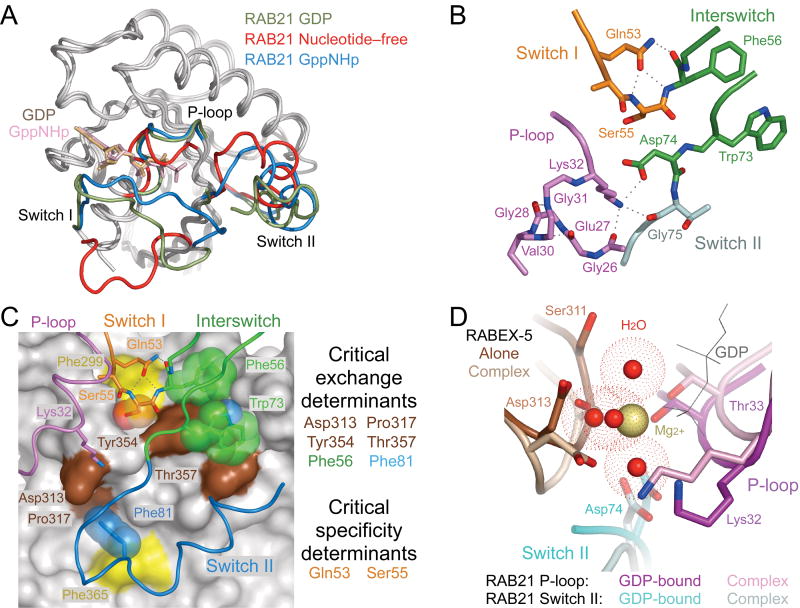
Figure 2.
Conformational changes accompanying formation of the nucleotide-free complex. (a) Superposition of GDP-bound (PDB 1Z0I (PDB 1YZU) RAB21 with the nucleotide-free form of RAB21 from the complex with RABEX-5. (b) Stabilization of the nucleotide-free state by intramolecular polar interactions. Dotted lines represent hydrogen bonds. (c) Correlation with critical exchange and specificity determinants identified in an earlier mutational analysis25. VPS9 domain of RABEX-5 is depicted as gray surface with critical exchange determinants highlighted in brown. Two additional residues discussed in the text are highlighted in yellow. RAB21 is depicted as a tube. Side chains with or without semitransparent spheres are shown for critical exchange or specificity determinants as well as other residues discussed in the text. (d) Steric crowding in the Mg2+-binding site following superposition of GDP-bound RAB21 (PDB 1Z0I) with nucleotide-free RAB21 from the complex with RABEX-5. Water molecules coordinated by the Mg2+ ion in GDP-bound RAB21 are depicted as red spheres surrounded by dot surfaces indicating the van der Waals radii.