Figure 2.
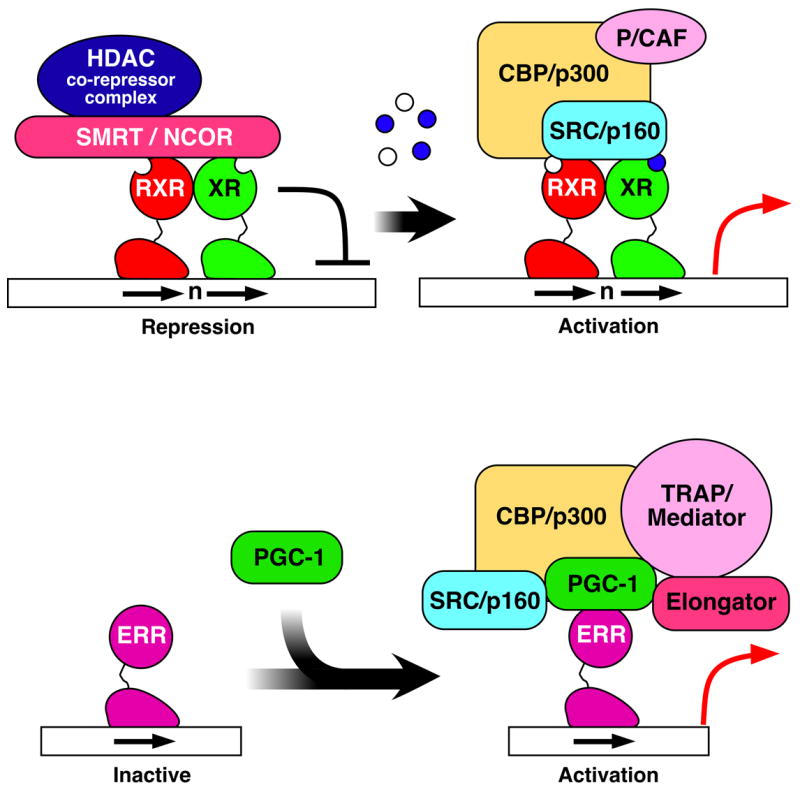
Schematic diagram for a typical NR activation mechanism. Top: In the absence of ligand, NRs form a repressive complex with HDACs (histone deacetylases) via corepressor SMRT or NCOR (left). Ligand binding induces a dissociation of corepressors and a recruitment of coactivators including HAT (histone acetyl-transferase) and chromatin remodeling complexes (right). Bottom: some nuclear receptors are activated by ligand-independendent binding of the PGC-1 coactivator and subsequent recruitment of additional coactivator complexes.
