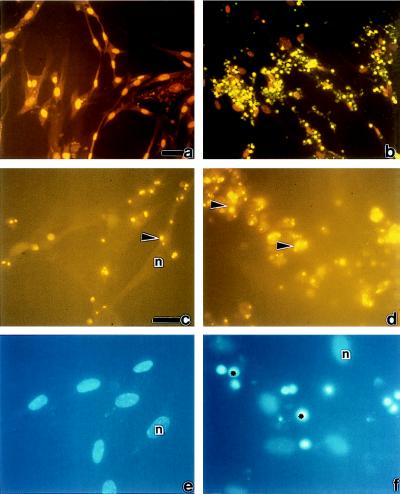
Figure 5.
Induction of apoptosis in wild-type and mutant HEF cells during R. rickettsii infection. Wild-type HEFs (a, c, and e) and HEFs stably transfected with a transdominant-negative IκBα mutant (b, d, and f) were infected with R. rickettsii for 18 hr and then subjected to TUNEL (a and b), immunofluorescence staining for R. rickettsii (c and d), and nuclear staining using Hoechst dye (e and f). c and e are identical fields as are d and f. Nuclei with normal morphology are denoted by n. Apoptotic nuclei in b and f are indicated by ∗. Arrowheads in c and d point to R. rickettsii organisms. (a and b Insets) Uninfected wild-type HEFs and uninfected mutant HEFs, respectively. [Bars = 5 μm (a for a and b) and 20 μm (c for c–f). Scoring of cells in these populations after TUNEL revealed that 74% of infected mutant HEFs were apoptotic and that 21% of infected wild-type HEFs were apoptotic.