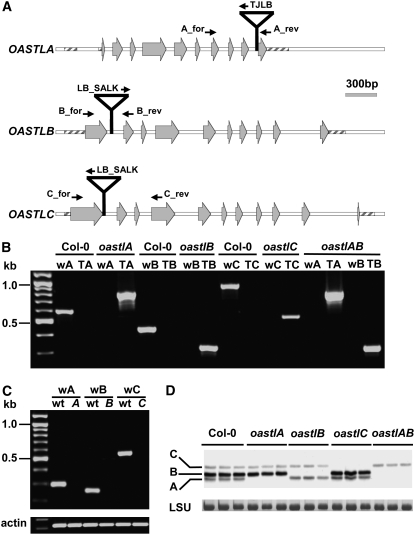
Figure 1.
Genomic Organization of oastl T-DNA Insertion Lines.
(A) Structures of genes OASTLA, OASTLB, and OASTLC are shown with insertion sites of T-DNAs in knockout plant lines. Exons are indicated by gray arrows, primers for the genetic characterization by small black arrows, and untranslated regions by striped boxes.
(B) Genomic characterization of T-DNA insertion lines. PCR with genomic DNA as template showed the presence of T-DNA in each oastl gene in the appropriate mutant; lack of the wild-type–specific product showed that the T-DNA allele was homozygous. Each wild type (w) and T-DNA (T) primer pair was specific for the gene of the indicated mutant.
(C) T-DNA insertions resulted in loss of mRNA of the three oastl genes as shown by RT-PCR. Amplification of actin from the same cDNA preparations was used as a positive control.
(D) Immunoblot of leaf protein extracts from the indicated oastl insertion lines (three lanes each) detected with a polyclonal antibody against Arabidopsis OAS-TL C. Cross-reaction with OAS-TL isoforms A and B shows the specific knockout of the indicated isoforms of OAS-TL in the mutants. Staining intensities of the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (LSU) protein in the same samples confirm equal loading in the individual lanes.