Fig. 3. Alpha adrenergic antagonists did not block the NE-induced outward current, increase in membrane conductance or Ih inhibition.
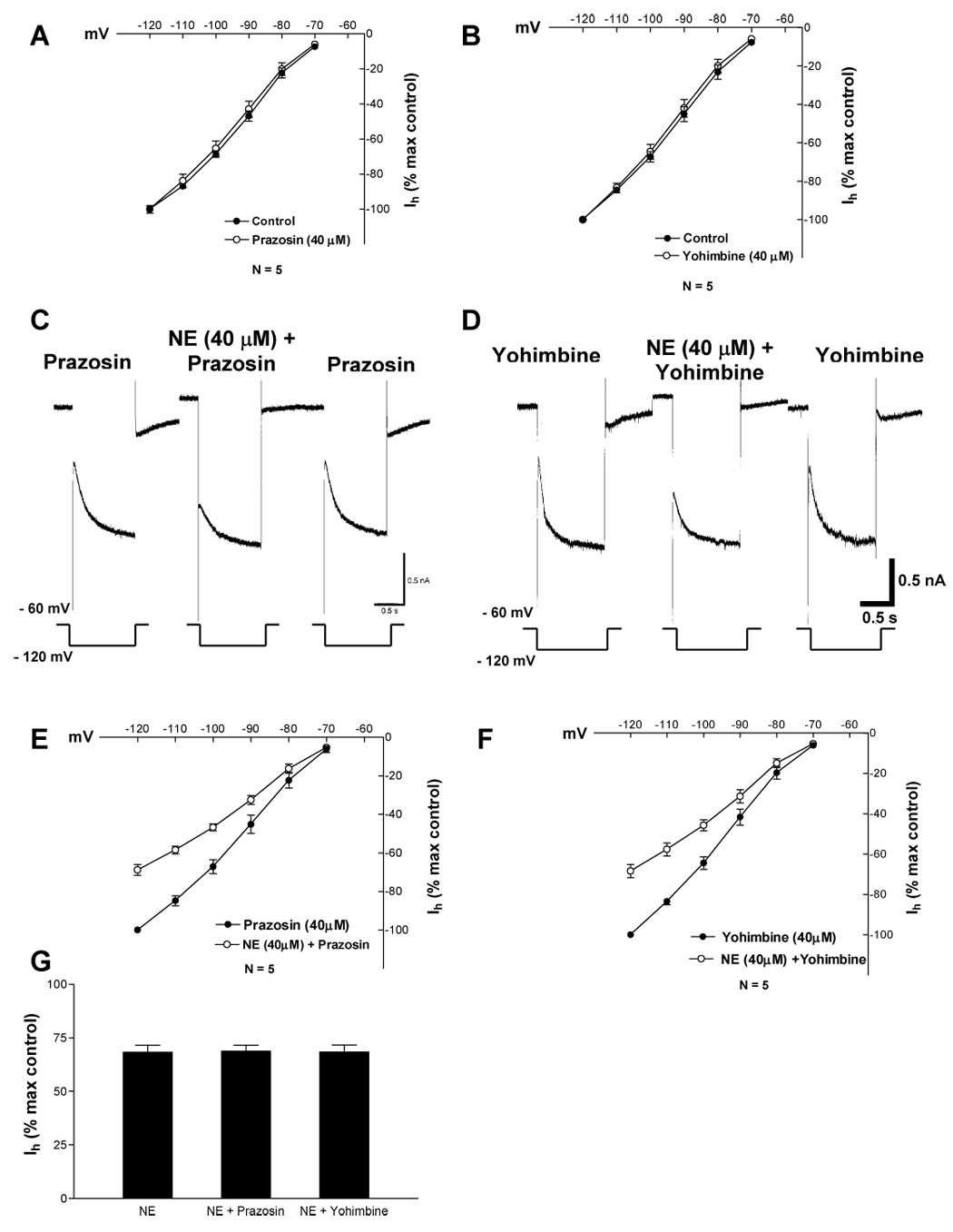
Data points on each graph represent average ± s.e.m. of five cells.
A. At 40 µM alpha-1 antagonist prazosin did not affect Ih amplitude.
B. At 40 µM alpha-2 antagonist yohimbine did not affect Ih amplitude.
C. In the presence of prazosin, NE evokes an outward current, increases the membrane conductance and inhibits Ih.
D. In the presence of yohimbine, NE evokes an outward current, increases the membrane conductance and inhibits Ih.
E. NE significantly reduced Ih amplitude in the presence of prazosin (2-way ANOVA, F=534.9, df = 1, 48;P < 0.0001).
F NE significantly reduced Ih amplitude in the presence of yohimbine (2-way ANOVA, F=99.72, df = 1, 48;P < 0.0001).
G. Maximal Ih inhibition (− 120 mV) in the presence of NE and prazosin or NE and yohimbine was not different from that of NE alone (1-way ANOVA, MS= 0.3481, df = 2, 19;P = 0.9956).
