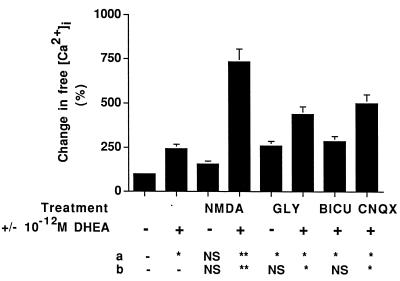
Figure 6.
Effect of NMDA, glycine and receptor antagonists on the increase of [Ca2+]i mediated by DHEA. Each bar shows the percent mean [Ca2+]i increase over baseline. Error bars are ±SEM of six separate measurements. NMDA (10 μM), glycine (10 μM), or antagonists (10 μM) were added to the cell suspension before addition of DHEA. NMDA increased [Ca2+]i above baseline values, and DHEA synergistically potentiated this response; glycine increased [Ca2+]i, and DHEA increased this response. Bicuculline (BICU) and 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) did not block the response of the cells to DHEA. These results support the involvement of the NMDA receptor in the DHEA-mediated increase in [Ca2+]i. Statistical differences between (a) control and treatments and between (b) DHEA treatment and other treatments (shown in a table at the bottom of the figure), were determined by using a two-way ANOVA test and post hoc Scheffe’s analysis; ∗∗, P < 0.001; ∗, P < 0.05.