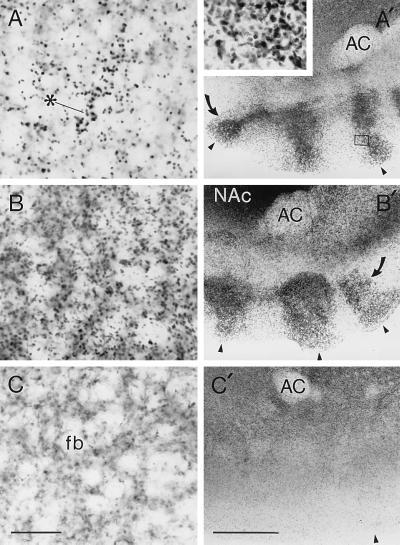
Figure 1.
Patterns of CREB phosphorylation in the dorsal and ventral striatum induced by D1-class dopamine receptor agonist stimulation (A and A′), stimulation of cAMP (B and B′), and of L-type Ca2+ channel activation (C and C′). Photomicrographs of PCREB immunostaining are shown for the caudoputamen (A–C) and the olfactory tubercle (A′–C′) of slice cultures treated for 30 min with different agonists. SKF-81297 induces CREB phosphorylation in striosomal patches of PCREB-positive nuclei (A, see asterisk), whereas forskolin induces expression of PCREB in many evenly distributed PCREB-positive nuclei in the caudoputamen (B). Box in A′ shows the region enlarged in the Inset. Both SKF-81297 (A′) and forskolin (B′) induce expression of strongly PCREB-positive nuclei in a horizontal band and ventral islands (curved arrows) in the olfactory tubercle. The L-type calcium channel agonist BAY K 8644 induces PCREB expression in the matrix of the caudoputamen (C), but it induces only low levels of PCREB expression in the olfactory tubercle (C′). The arrowheads in A′–C′ indicate the bottom edges of the sections. AC, anterior commissure; NAc, nucleus accumbens; fb, fiber bundles. [Bar in C (for A–C) = 100 μm; bar in C′ (for A′–C′) = 0.5 mm.]