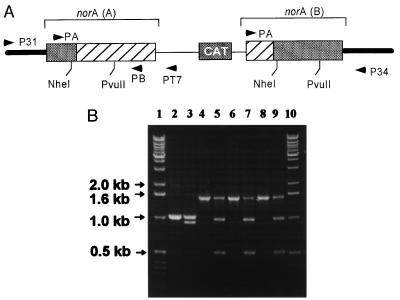
Figure 1.
Disruption of the chromosomal norA gene by homologous recombination. (A) The shaded bars represent the N-terminal and C-terminal portions of norA originating from the chromosome, and the hatched boxes represent portions of the norA sequence originating from integration of plasmid PCH23 lacking N- and C-termini. The resultant norA(A) lacks a C terminus and the resultant norA(B) lacks an N terminus. Primer P31 corresponds to a sequence 450 bp upstream the norA gene. Primer PT7 corresponds to the T7 promoter sequence of plasmid PCH23. (B) Using primers P31 and PT7, a 1.5-kb fragment was expected to be amplified if norA was disrupted in a manner shown in A. Lanes: 1 and 10, DNA markers; 2, PCR product amplified with primers A and B from chromosomal DNA of wild-type cells (positive control, expected size, 1 kb); 3, DNA from lane 2 digested incompletely by NheI; 4, 6, and 8, PCR products using P31 and PT7 primers and chromosomal DNA from KLE 820, KLE 821, and KLE 822, three independent putative norA disruption clones, respectively. There was no product with primers P31 and PT7 using wild-type chromosomal DNA (not shown). Lanes 5, 7, and 9, PCR products of lanes 4, 6, and 8 digested incompletely with NheI. The structure of the construct was verified further by obtaining an expected 1.4-Kb PCR product with primers PA and P34. Primers P31 and P34 produced an expected 1.7-Kb PCR product from the wild type but not from KLE 820 (not shown).