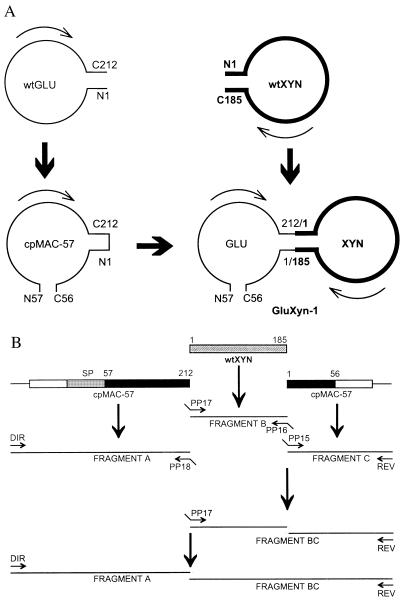
Figure 1.
Design and construction of GluXyn-1. (A) Schematic structure of GluXyn-1 and the parental enzymes used for the construction of the bifunctional insertion fusion protein. The circularly permuted cpMAC-57 (9) starts with residue 57 of wtGLU whereas the original N and C termini are covalently linked leading to an enzyme whose C terminus is residue 56. cpMAC-57 and wtXYN (bold line) were linked by cutting the loop between residues 212 and 1 of cpMAC-57 (numbering according to GLU) and connecting those residues with the terminal residues of XYN. The resulting construct, GluXyn-1, starts with N57 and ends with C56 just as cpMAC-57, but contains in its central part the full-length sequence of mature XYN. For simplicity, only the sequences encoding the mature enzymes are shown. Amino acid residues in GluXyn-1 are numbered according to their sequence positions in the parent proteins, wtGLU and wtXYN, throughout this paper. (B) Construction of GluXyn-1 by PCR splicing of gene fragments. Fragment A covers the upstream regulatory sequence of the gene encoding the B. macerans 1,3–1,4-β-glucanase (open box) and sequences encoding the signal peptide (SP) and the mature 1,3–1,4-β-glucanase from residues 57 to 212 (solid box). Fragment B encodes the full-length mature XYN, and fragment C consists of the coding region for residues 1–56 of B. macerans β-glucanase (solid box) and a short segment of the 3′ noncoding region of cpMAC-57 (open box). Using sequence specific primers, the three fragments were amplified by splicing-by-overlap extension whereby terminal extensions complementary to the adjacent sequence in the resulting GluXyn-1-encoding construct (shaded box) were linked to the synthesized fragments. In the second (fragments B and C) and third step of amplification (fragments A and BC) the obtained fragments were used to amplify the full-length hybrid gene encoding GluXyn-1. Sequence specific primers PP15-PP18 are indicated by arrows. Direct (DIR) and reverse (REV) primers annealing with the flanking vector sequences also are shown.