Figure 1. Nrf2 and Keap1 homologues are conserved in Drosophila.
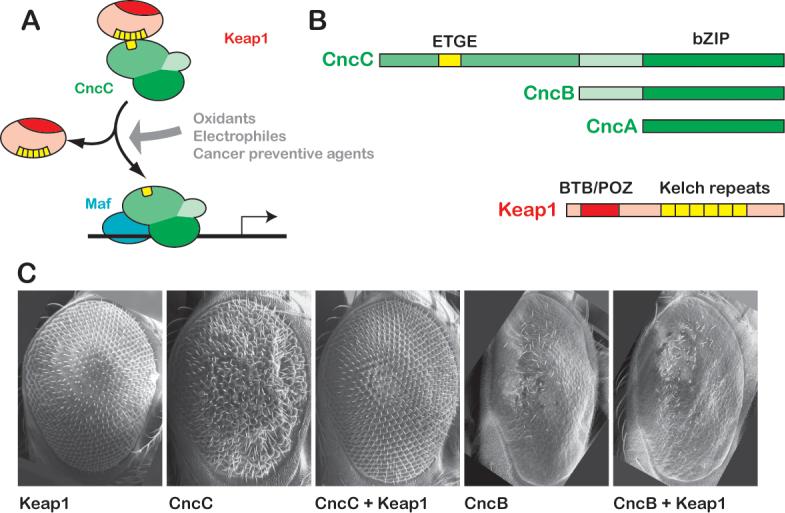
A. The Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. In basal conditions, Keap1 binds to Nrf2 and inhibits its activity. Oxidative stressors, electrophilic xenobiotics, and cancer chemopreventive agents releave this inhibition. Stabilized Nfr2 then accumulates in the nucleus and dimerizes with a small Maf protein to transcriptionally activate a battery of cell protective genes. B. Nrf2 and Keap1 homologues are present in Drosophila. The cnc locus of Drosophila encodes three protein products. All contain the bZIP region that mediates dimerization and DNA binding. Only the longest isoform, CncC, contains domains predicted to bind Keap1, including the ETGE motif, and is thus potentially a Nrf2 homologue. The Drosophila Keap1 protein shows a high degree of sequence similarity to its vertebrate Keap1 counterparts (sequence alignments for CncC and Keap1 proteins are shown in Supplemental Fig 1). Conserved domains include the BTB/POZ domain required for dimerization and 6 Kelch repeats for binding to Nrf2 and anchoring to actin. C. Over-expression of Drosophila Keap1 can inhibit CncC activity in vivo. Expression of CncC in the developing Drosophila eye from a UAS transgene under the control of sepGal4 causes a reproducible aberrant phenotype. Over-expression of Keap1 under the same conditions (or with GMRGal4, data not shown) has no phenotypic effect, but it can completely suppress the effects of CncC over-expression. The activity of the shorter CncB isoform, which lacks the putative Keap1-interacting domain, is not inhibited by Keap1 co-expression. The GMRGal4 driver was used to express CncB (and Keap1) in the rightmost two panels of C., because expression by sepGal4 did not produce a phenotype at 25°C.
