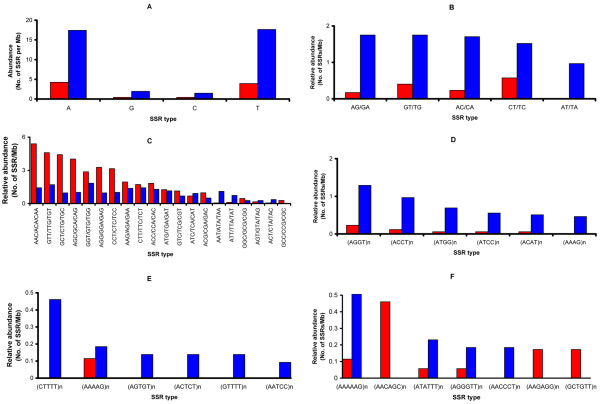
Figure 2.
Genome-wide distribution of relative abundance of SSRs by the SSR types in different SSR unit number. The relative abundances of SSRs are presented by the genome region: genic region (red bar) and non-genic region (blue bar). Each panel represents a different SSR type: mono-nucleotide SSR (A), di-nucleotide SSR (B), tri-nucleotide SSR (C), tetra-nucleotide SSR (D), penta-nucleotide SSR (E), and hexa-nucleotide SSR (F). From tetra-nucleotide SSR (D), the possible repeats of each microsatellite type are shown as (nucleotide sequence)n. For example, (AGGT)n stands for AGGT/GGTA/GTAG/TAGG repeats. The x-axis represents the different sequence types and the y-axis represents relative abundance where the observed count of SSRs in each category is divided by megabase of sequence.