FIGURE 1.
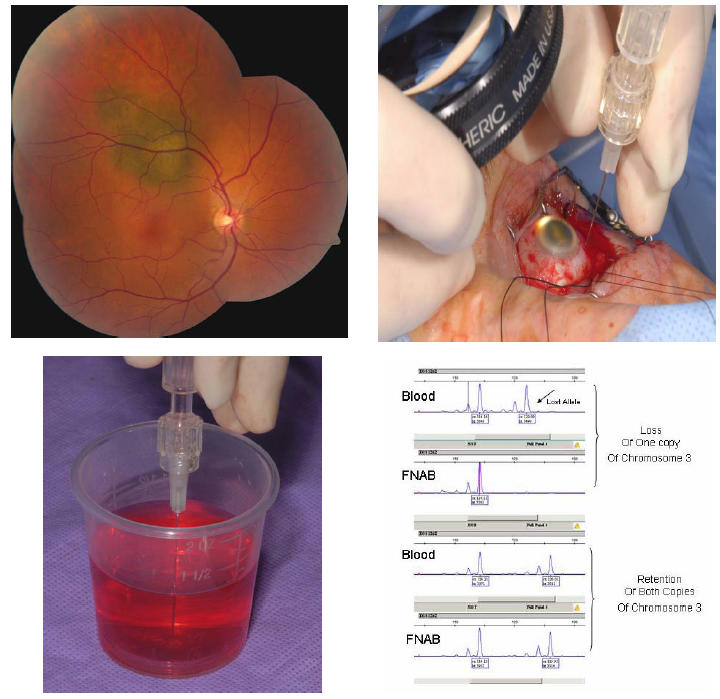
Technique of fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) for genetic analysis of uveal melanoma. Top left, Small choroidal melanoma with overlying orange pigment and subretinal fluid. Genetic testing confirmed monosomy 3. Top right, At the time of surgery, the tumor is localized and nylon sutures for securing the radioactive plaque are placed in the sclera. Immediately before placement of the radioactive plaque, FNAB is performed through the par plana using a 27-gauge long needle. The tumor sample is taken from an extramacular portion of the tumor, taking care to avoid the major retinal vessels. A small amount of localized vitreous hemorrhage at the site of tumor penetration is expected. Bottom left, The microscopic sample is aspirated into the syringe with pink Hanks solution and then flushed into a test tube for analysis by the genetics laboratory. Bottom right, Microsatellite assay displaying two different samples. The top example shows blood results (normal peripheral blood lymphocyte DNA) with both copies of chromosome 3, but the FNAB of the choroidal melanoma showed loss of 1 copy (monosomy 3). The bottom sample shows blood results with both copies of chromosome 3 and the FNAB of the choroidal melanoma showed retention of both copies (disomy 3).
