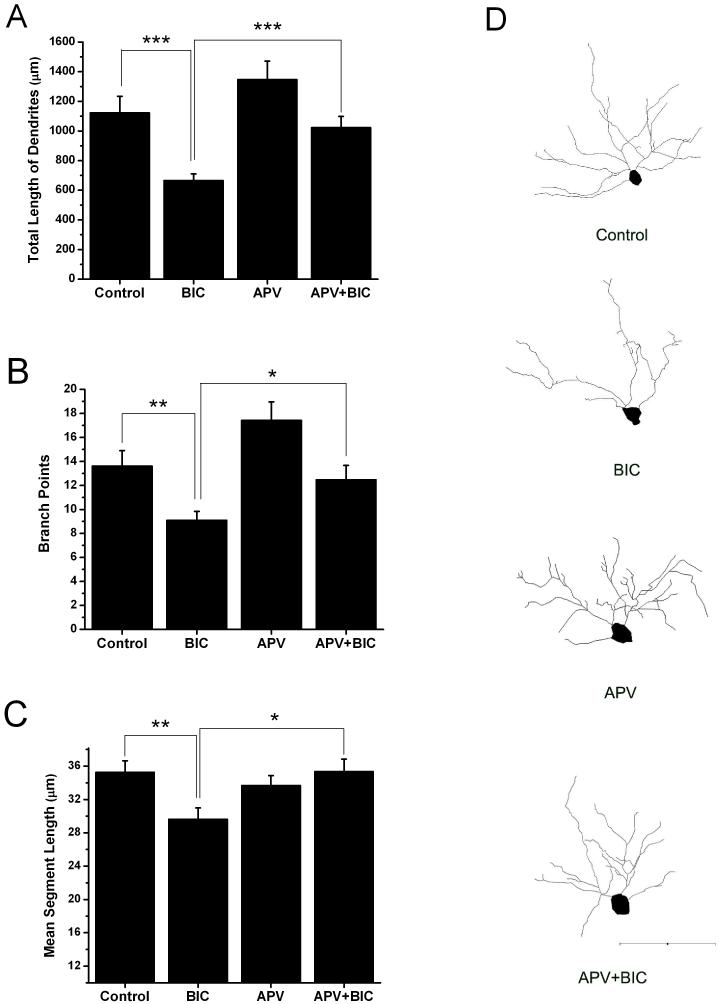
Fig. 5.
The NMDA receptor antagonist APV blocks bicuculline-induced reductions in dendritic arborization. Bar graphs show that the total length of CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cell dendrites (A), the number of branch points (B) and mean segment length (C) were all reduced by bicuculline when compared with that of control. APV alone did not significantly alter these measures of dendritic morphology but when slices were co-treated with APV and bicuculline the bicuculline-induced effects were eliminated. Only treatment with bicuculline differed statistically from controls. (D) Representative Neurolucida reconstructions of the soma and basilar dendrites of YFP positive CA1 pyramidal neurons from the four treatment groups. Number of neurons reconstructed: Control n=18, Bicuculline n=20. APV n=19, APV+BIC n=17. Scale bar = 100 μm. (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001)