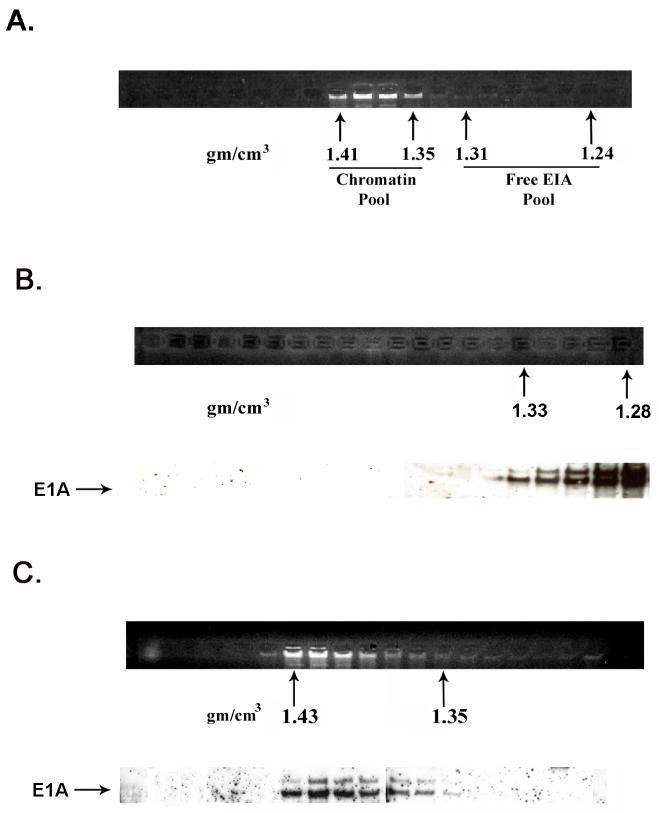
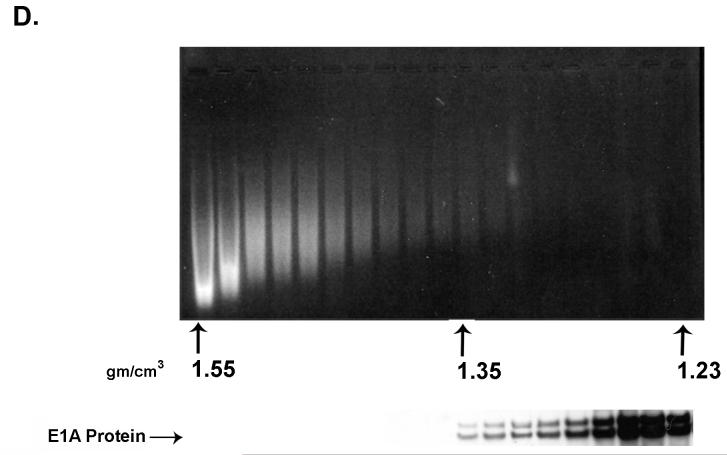
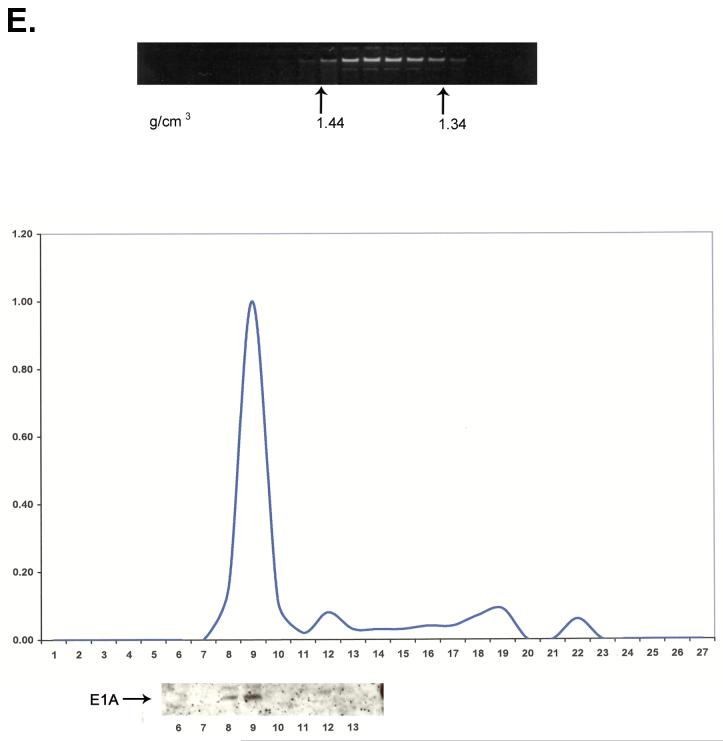
Fig. 1.
A portion of E1A proteins in HEK 293 cells is closely associated with chromatin. Chromatin from formaldehyde cross-linked 293 cells was subjected to isopycnic centrifugation on CsCl gradients. (A) Fractions containing chromatin and fractions at the top of the gradient containing free proteins were separately pooled and subjected to a second CsCl centrifugation. (B) EtBr staining and E1A immunoblot analysis of the second CsCl gradient of the “free E1A pool” showing that free E1A proteins band reproducibly at the top of the gradient. (C) EtBr staining and E1A immunoblot analysis of the second CsCl gradient of the “chromatin pool” showing that E1A protein associated with chromatin faithfully co-equilibrates with chromatin after a second CsCl gradient. (D) E1A proteins in HEK 293 cells not cross-linked with formaldehyde dissociate from chromatin DNA in the high salt conditions of a CsCl gradient. EtBr staining and E1A immunoblot shows that all E1A proteins equilibrate at the top of the gradient and are not artificially associated with DNA at the bottom of the gradient. (E) E1A proteins in formaldehyde cross-linked 293 cells remain closely associated with chromatin after stringent purification. (Upper panel) Chromatin from cross-linked 293 cells was subjected to isopycnic centrifugation on a CsCl gradient. (Lower panel) Chromatin containing fractions from the CsCl gradient were pooled and subjected to Superose 12 size exclusion chromatography. E1A remained closely associated with chromatin in the excluded fractions (fractions 8 and 9) as indicated by immunoblot analysis. Y-axis values are absorbance at A280.