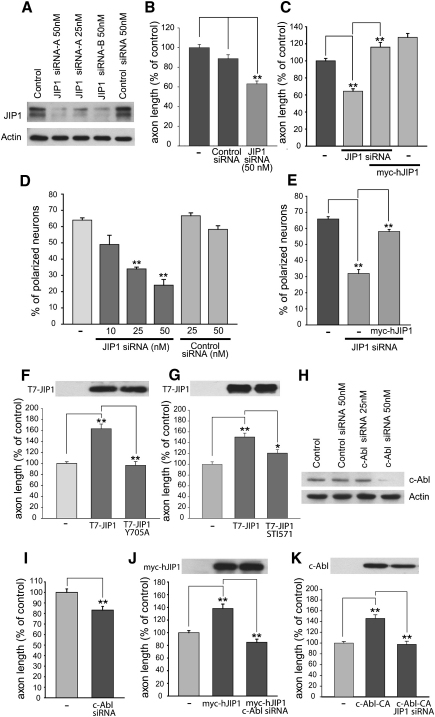
Figure 2.
JIP1 Regulates Axon Length and Neuronal Polarization
(A) Immunoblot demonstrating a reduction in JIP1 protein levels with the use of two different JIP1 siRNAs but not with nonspecific control siRNA (72 hr after transfection).
(B) Axonal length of cortical neurons was evaluated 72 hr after cotransfection with JIP1 siRNA and eGFP.
(C) The decrease in axonal length after JIP1 siRNA was rescued by expression of myc-tagged human JIP1.
(D) Measurement of the number of polarized neurons in developmentally delayed cortical neurons (see Supplemental Data) transfected with JIP1 siRNA and eGFP.
(E) Ectopic expression of myc-tagged human JIP1 rescues the decrease in neuronal polarization observed with JIP1 siRNA. For polarization experiments, data are expressed as percent of total number of neurons (mean ± standard error of the mean [SEM], from six independent experiments and ∼250 neurons counted for each condition).
(F, G, and I–K) Neurons were transfected with constructs expressing either wild-type JIP1, a JIP1 mutant that does not bind to kinesin-1 (JIP1-Y705A), c-Abl siRNA, myc-hJIP1, constitutively active c-Abl (c-Abl-CA), or JIP1 siRNA as indicated. Where indicated, the c-Abl inhibitor STI-571 (1 uM) was added to cultures 14 hr prior to cell lysis. JIP1 expression levels were detected with anti-T7 and anti-myc tag antibodies, and c-Abl was detected with a c-Abl antibody.
(H) Immunoblot for c-Abl protein levels after transfection with c-Abl siRNA. For all measurements of axonal length, the data are expressed as percent of respective controls (mean ± SEM, from six to eight independent experiments and ∼100 axons measured for each condition). Statistical significance was determined via one-way ANOVA, with post hoc Tukey's test for comparison between groups. Values of p < 0.05 (∗) were taken to be statistically significant, (∗∗) indicates values of p < 0.001.