Figure 1.
Outline of the TEV-Cleavage System
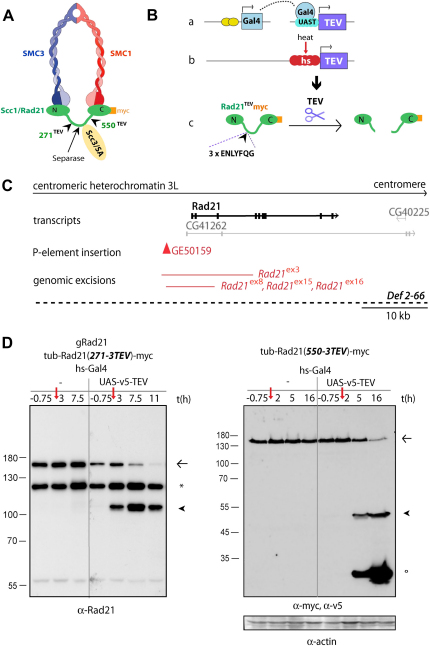
(A) Schematic of the cohesin complex containing TEV-cleavable Rad21 (green), SMC1 (red), SMC3 (blue), and Scc3/SA (yellow). Cleavage of Rad21 by separase occurs in the flexible linker region. Arrowheads indicate the sites of insertion of TEV-recognition sequences (numbers refer to amino acid positions).
(B) Outline of the TEV-cleavage system showing two alternative methods to express TEV in vivo in flies. (a) UAS-TEV is controlled by the UAS/GAL4 system, enabling TEV expression by specific Gal4 driver lines. (b) TEV directly fused to the heat-shock promotor allows for its ubiquitous induction in a time-specific manner. (c) Once expressed, catalytically active TEV protease cleaves Rad21TEV.
(C) Representation of the genomic region of the Rad21 locus. The Rad21 gene (CG17436) resides in the centric heterochromatin of chromosome 3L. The exon-intron structure of the Rad21 mRNA is shown in bold. EST-based transcript predictions of neighboring genes are depicted in lighter gray. The EP element GE50159 4 kb upstream of the transcriptional start of Rad21 is represented by a red triangle. The four independently generated imprecise excision mutants of Rad21 lack the chromosomal intervals indicated by solid, red lines. The Rad21 locus is missing in the γ-ray-induced deficiency Def 2-66 (dashed line). The scale bar is 10 kb.
(D) Pupal protein extracts were prepared before (t = −0.75 hr) and at different time points after a 45 min heat shock at 37°C (red arrow). Western blot analysis with antibodies against endogenous Rad21 (left panel) or myc (right panel) shows full-length Rad21TEV (arrow) and the C-terminal TEV-cleavage product (arrowhead) as well as gRad21 (asterisk). V5-tagged TEV protease is detected by probing with v5 antibodies (open circle). Actin was used as a loading control. A molecular weight marker (in kDa) is shown on the left.