Figure 2.
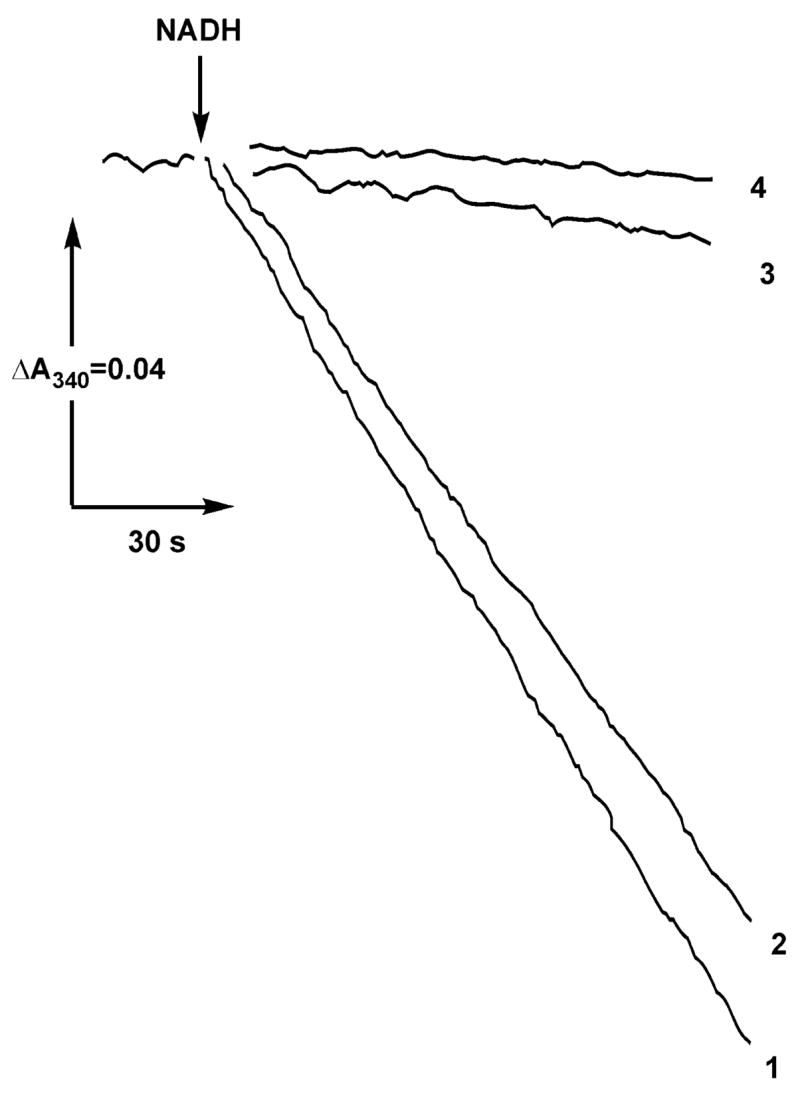
Rapid irreversible decomposition of NADH-OH by HAR and the resistance of the enzyme-bound inhibitor to the electron acceptor. Actual tracings of the NADH:HAR reductase activities after preincubation with NADH-OH and HAR are shown. (Curve 1) SMPs (25 μg/mL) were incubated for 1 min in the standard reaction mixture containing 0.5 mM HAR, and the reaction was initiated by the addition of 100 μM NADH and 5 μM rotenone as indicated. (Curve 2) NADH-OH (28 nM) was preincubated in the standard mixture containing 0.5 mM HAR for 1 min, 25 μg/mL of SMPs were then added following 1 min of incubation, and the reaction was initiated by the addition of NADH and rotenone. (Curve 3) SMPs (25 μg/mL) were incubated for 1 min with 28 nM NADH-OH, 0.5 mM HAR was added following 1 min of incubation, and the reaction was initiated by the addition of NADH and rotenone. (Curve 4) Same as curve 3. The reaction was initiated by simultaneous addition of NADH, HAR, and rotenone.
