Figure 1.
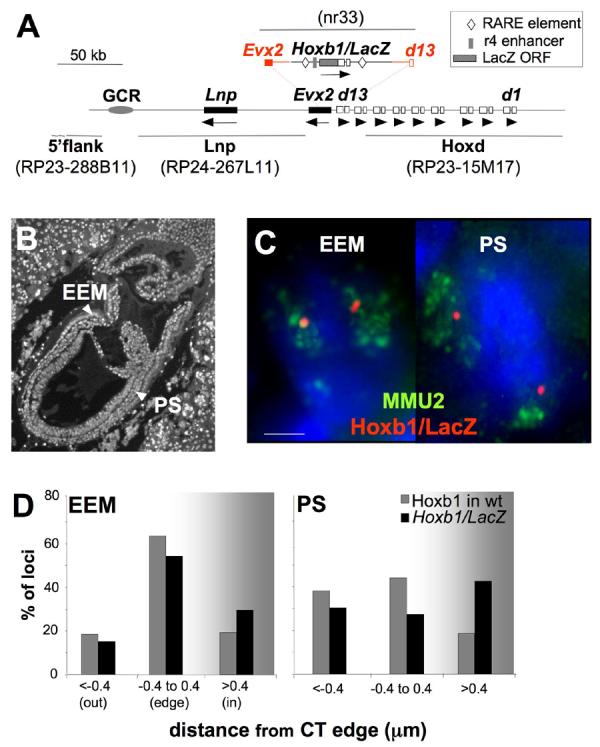
Looping out of Hoxb1/LacZ from the chromosome territory occurs in the PS of E7.5 transgenic embryos. (A) Map of the Hoxd locus on MMU2 showing the structure and the integration site of the Hoxb1/LacZ transgene. The extent of the homology arms used for recombination are shown in red and the Hoxb1 cis-regulatory retinoic acid response elements (RAREs) and the r4 enhancer included in the transgene are depicted (Kmita et al., 2000). Exons of Hoxd genes from Hoxd1 (d1) to Hoxd13 (d13) are shown as open boxes; other genes in the region are shown as black boxes. The orientation of transcription is indicated by arrows underneath the genes. The grey oval locates a region of non-coding sequence conservation that overlaps the Global Control Region (GCR) (Spitz et al., 2003). The location of the BACs and the Hoxb1/LacZ plasmid used as FISH probes are shown in grey. (B) DAPI staining of a 4μm E7.5 embryo section used for the FISH analysis showing the nuclei of the PS and EEM. (C) Maximal projection image after deconvolution of 3D FISH using the Hoxb1/LacZ probe (red) hybridised together with a MMU2 chromosome paint (green) on DAPI counterstained nuclei of the EEM or the PS of E7.5 Hoxb1/LacZ embryos. Scale bar: 2 μm. (D) Histograms showing the 3D position of hybridisation signals for the Hoxb1/LacZ transgene relative to the MMU2 CT edge (black bars), or for endogenous Hoxb1 relative to the edge of the MMU11 CT (grey bars) in nuclei from the EEM and PS of E7.5 transgenic or wild-type (wt) embryos respectively. Loci are defined as outside of the CT if the distance measured is > 0.4μm beyond the visible limits of the CT hybridisation signal.
