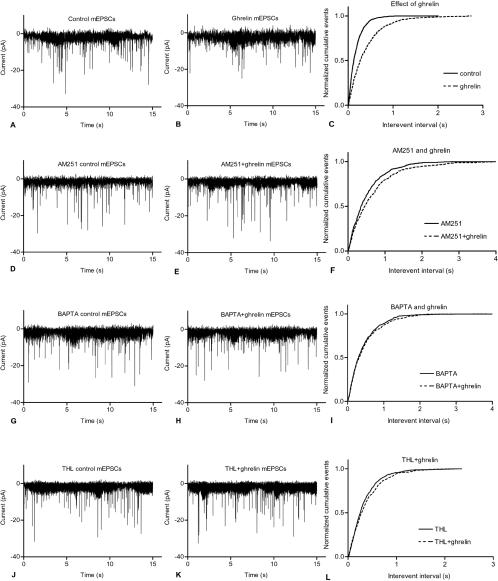
Figure 2. Whole-cell patch clamp recordings of mEPSCs in the parvocellular neurons of the PVN.
Application of ghrelin (100 nM) in the extracellular solution decreased the amplitude and frequency of the mEPSCs (Fig. 2A–C). Extracellular administration of the cannabinoid receptor antagonist AM251 (1 µM), however, blocked the effect of ghrelin. Both amplitude and frequency changes were attenuated (Fig. 2D–F). In addition, intracellularly applied BAPTA, an effective chelator of free calcium, (Fig. 2G–I) and the DAG lipase (DAGL) inhibitor THL (5 µM) (Fig. 2J–L) also abolished the effect of ghrelin.