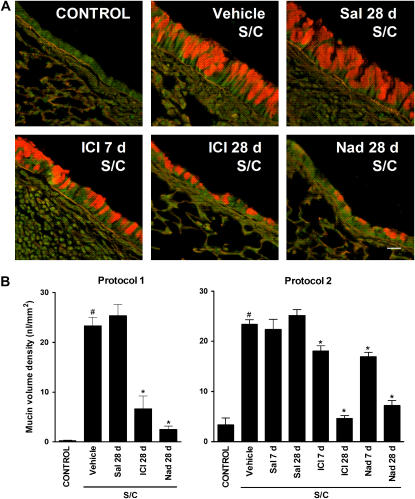
Figure 4.
Effects of chronic administration of beta-adrenoceptor ligands on mucin content in the airway epithelium. Mucin content in the airway epithelia of BALB/cJ mice was measured using periodic acid fluorescent Schiff from (A) saline-challenged mice (CONTROL), antigen-challenged mice (S/C) administered vehicle, the beta2-adrenoceptor agonist salbutamol for 28 days (Sal 28 d), the selective beta2-adrenoceptor antagonist ICI 118,551 for 7 or 28 days (ICI 7 or 28 d), or the nonselective beta-adrenoceptor antagonist nadolol for 28 days (Nad 28 d) (Figure 1, protocol 1). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Morphometric quantification of the mucin volume density was assessed from the various groups (left panel using protocol 1 of Figure 1). A second set of experiments was performed to assess the effect of beta-adrenoceptor ligands administration during the challenge phase only (right panel using protocol 2 of Figure 1). Values are the means ± SEM of data from 3 to 10 mice in each group (n = 3–10). #P < 0.05, significantly different compared with saline-challenged mice; *P < 0.05, significantly different compared with antigen-challenged mice.