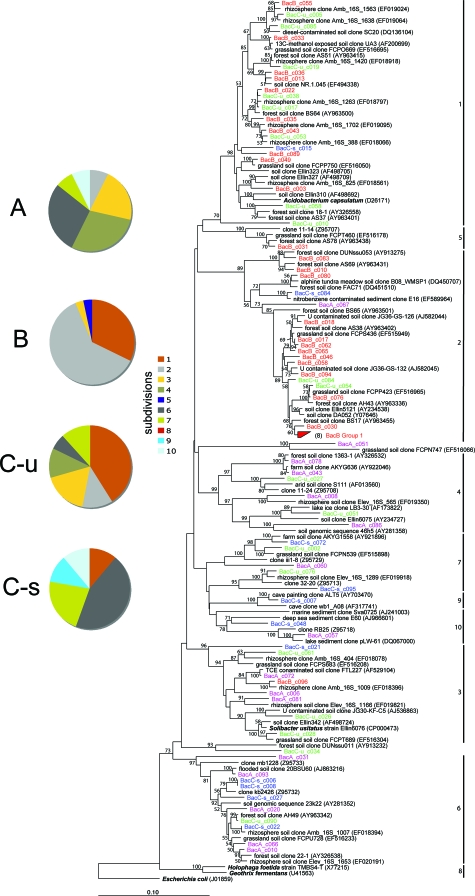
FIG. 2.
Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of Acidobacteria-affiliated 16S rRNA sequences for the A, B, unsaturated C (C-u), and saturated C (C-s) horizons. As identified by Zimmerman et al. (94), intersubdivision tree topologies differ depending on the tree-building methods (e.g., neighbor joining, maximum parsimony, or maximum likelihood) utilized, yet relationships within subdivisions are consistently stable regardless of the algorithm utilized. Here we utilize the distance-based neighbor-joining method, which results in a different ordering of the previously assigned subdivision numbers while maintaining a stable branching order within each subdivision. Bootstrap values (n = 1,000) of greater than 50% are indicated at nodes. Escherichia coli is the outgroup.