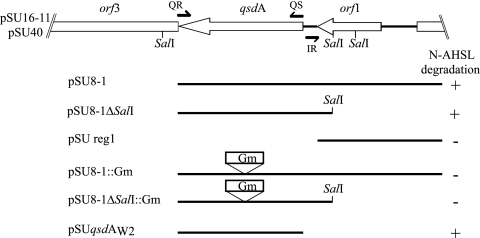
FIG. 2.
Identification of the qsdA gene. The genetic organization of the qsdA locus derived from the complete sequence of the 3.2-kb EcoRI fragment conferring C6-HSL degradation upon its host is shown at the top. Broken arrows symbolize the primers used for subcloning and their orientations. Restriction sites also used for subcloning are shown. See Table 1 for a description of the plasmids. Plasmid constructions used to identify the qsdA gene were assayed for their ability (+) or inability (−) to confer N-AHSL degradation upon their host against a set of N-AHSLs, including C6-HSL, O-C6-HSL, C7-HSL, C8-HSL, O-C8-HSL, O-C10-HSL, C12-HSL, O-C12-HSL, and O-C14-HSL. Each construct gave identical degradation results regardless of the N-AHSL present in the medium.