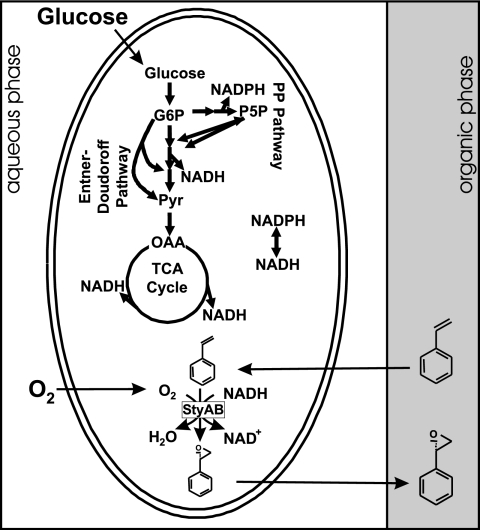
FIG. 1.
Schematic of the two-liquid-phase whole-cell styrene epoxidation system. The central carbon metabolism of recombinant E. coli fueled with glucose produces biomass precursors, energy, and the reduced redox coenzymes, which serve as electron donors for the epoxidation of styrene catalyzed by the styrene monooxygenase StyAB of Pseudomonas sp. strain VLB120. Thereby, molecular oxygen serves as an oxygen donor and the presence of the organic phase minimizes the aqueous concentrations of toxic styrene and styrene oxide. OAA, oxaloacetate; P5P, pentose-5-phosphates..