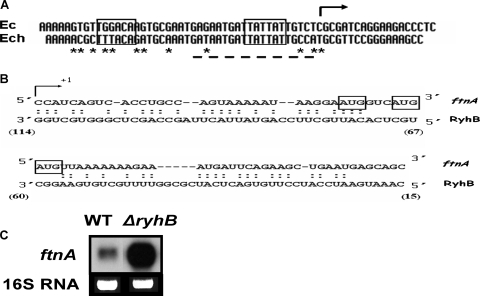
FIG. 7.
Occurrence of a ryhB gene in E. chrysanthemi. (A) Sequence alignment of the promoters of the ryhB genes of E. coli (Ec) and E. chrysanthemi 3937 (Ech). The −35 and −10 promoter elements are boxed, and the potential Fur box is underlined. The transcriptional start identified in E. coli is indicated by an arrow. Nonconserved nucleotides are indicated by asterisks. (B) Sequence complementarity between the E. chrysanthemi RyhB RNA and the 5′ part of the ftnA transcript. The identified transcriptional start of the ftnA gene is indicated by an arrow, and the potential translational starts are boxed. Numbers indicate nucleotide positions in RyhB RNA. (C) Northern blot analysis of E. chrysanthemi ftnA messenger accumulation in the wild-type (WT) strain and the ΔryhB mutant. Total RNAs were extracted from cells at the late exponential growth phase, and 3 μg of RNA was blotted as described in Materials and Methods. Northern blot analysis was performed as described in Materials and Methods.