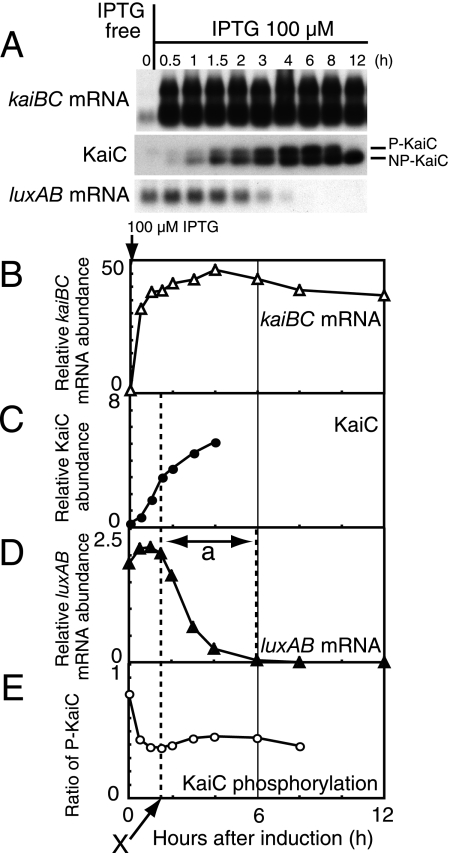
FIG. 2.
Transcriptional repression of the kaiBC promoter activity by kaiBC overexpression. (A) Temporal profiles of kaiBC mRNA accumulation (Northern blot analysis; upper panel), KaiC protein accumulation (Western blot analysis; middle panel), and luxAB mRNA accumulation (Northern blot analysis; lower panel) in NUC0220 after the addition of 100 μM IPTG. Cells for analysis were collected before induction (hour 0) and 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, and 12 h after induction. Total protein (0.5 μg) and total RNA (1 μg) were used for the analyses. In the middle panel, the upper band represents the phosphorylated forms of KaiC (P-KaiC), and the lower band corresponds to the unphosphorylated form (NP-KaiC). The data shown are representative of at least five independent experiments. (B to E) Quantitative estimation of kaiBC mRNA (B), KaiC protein (C), luxAB mRNA (D), and the phosphorylation ratio of KaiC (E). The phosphorylation ratio of KaiC was calculated as the ratio of phosphorylated KaiC to total KaiC (from panel A). The signals from Western and Northern blot analyses were measured by densitometry. Relative accumulation levels were calculated (see Materials and Methods) and plotted against time after the addition of 100 μM IPTG. Due to the smearing of NP-KaiC signal to the P-KaiC position, data for hour 12 are not shown in Fig. 2E. Dashed lines and the arrow (“X”) indicate the time point at which luxAB mRNA levels (which reflected kaiBC promoter activity) began to decrease. “a” indicates the transition time for repression of PkaiBC to baseline level.