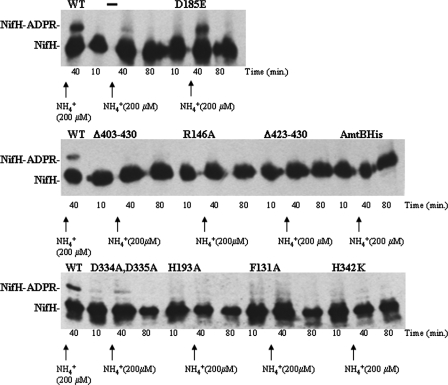
FIG. 3.
Ammonium-induced ADP-ribosylation of NifH in amtB variant strains. Cultures of R. capsulatus were grown under N2-fixing conditions. Time zero corresponded to the addition of acetylene necessary to start the in vivo nitrogenase activity assay (results presented in Table 1) which was carried out simultaneously with the monitoring of the ADP-ribosylation state of NifH. Where indicated by arrows, NH4Cl was added to 200 μM at 25 min. Culture samples were withdrawn at the indicated times, and the ADP-ribosylation state of NifH of the amtB mutant strain (RCAY63) complemented with the wild-type glnK-amtB operon encoding wild-type AmtB (WT), the uncomplemented amtB mutant strain (−), and the amtB mutant strain complemented with plasmids carrying glnK-amtB operons bearing different mutated amtB genes encoding AmtB variants (D185E, Δ403-430, R146A, Δ423-430, AmtBHis, D334A D335A, H193A, F131A, and H342K) was monitored by immunoblotting.