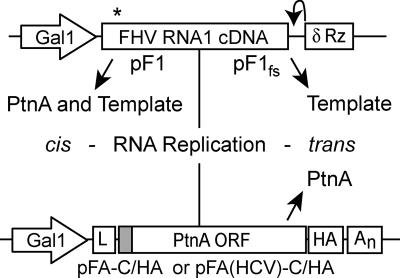
FIG. 1.
Schematics of FHV replicons. RNA replication in cis (left) is initiated when wild-type FHV RNA1 is transcribed from plasmid pF1 by host RNA polymerase II. Authentic 5′ and 3′ ends are generated by precise transcription initiation and a hepatitis delta ribozyme (δ Rz), respectively, and therefore RNA1 from pF1 can both be translated into protein A (PtnA) and function as an RNA replication template. RNA replication in trans (right) requires that the replication template and PtnA be provided by separate plasmids. The RNA1 template is transcribed from plasmid pF1fs, which contains an early frameshifting mutation (asterisk) that introduces a premature stop codon. Functional protein A is provided in trans from a second plasmid, either pFA-C/HA or pFA(HCV)-C/HA, which generates mRNAs with modified 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions that optimize their translation by introduction of the GAL leader (L) and CYC1 polyadenylation signal (An) but prevent their utilization as replication templates. The shaded box indicates the location of the membrane-targeting signal that is modified in pFA(HCV)-C/HA.