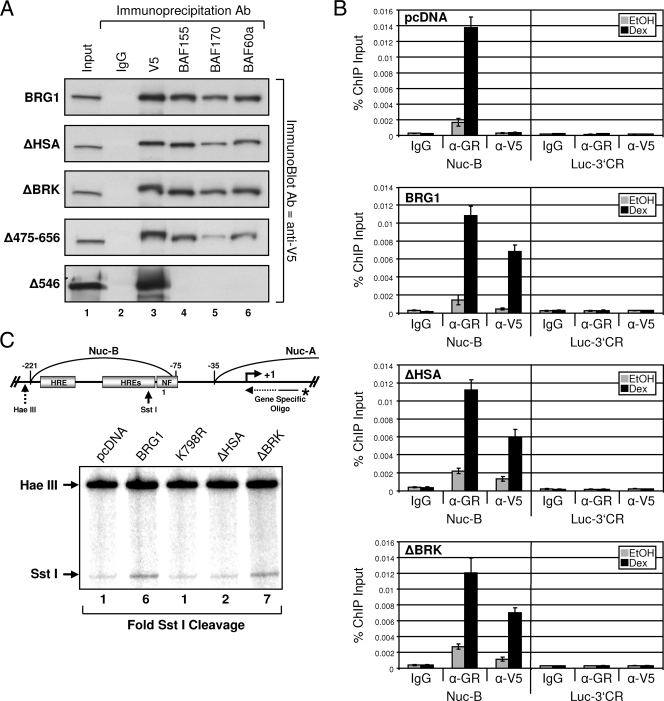
FIG. 3.
BRG1 mutants interact with core SWI/SNF subunits, display GR-dependent promoter binding, and require the HSA domain for remodeling activity. (A) Complexes containing BRG1 and mutant BRG1 were immunopurified from transfected SW-13 cells using antibodies (Ab) specific for V5 epitope, BAF155, BAF170, and BAF60a. Immunoprecipitates were resolved by 6% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-V5 antibody. Normal IgG was used to detect nonspecific interactions. (B) BRG1-, ΔHSA-, and ΔBRK-containing complexes are recruited to stably integrated MMTV in a GR-dependent manner in SW-13 cells, as demonstrated by ChIP analysis using anti-V5 antibody (α-V5). Purified immunoprecipitated DNA fragments were analyzed by real-time PCR using primer sets covering the MMTV promoter (Nuc-B) or 3′-coding region of the luciferase reporter (Luc-3′CR). Data were displayed as the percentages of ChIP input. Normal IgG was used as a negative control. Data represented are from three independent experiments. EtOH, ethanol. (C) In vivo restriction enzyme accessibility assay to determine MMTV chromatin structure. Nuclei were purified from treated (EtOH or Dex) cells expressing GR and BRG1 or mutant proteins followed by incubation with SstI (in vivo). Purified products were further digested to completion with HaeIII (in vitro) and used as a template for reiterative primer extension with an MMTV-specific primer. Extension products were resolved by 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Change in SstI cleavage is indicated below the gel. HRE, hormone response element; Oligo, oligonucleotide.