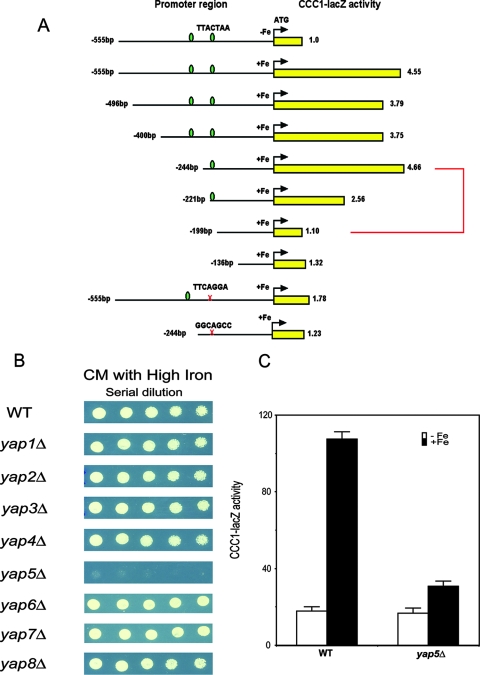
FIG. 3.
Yap5 is responsible for the iron-dependent transcription of CCC1. (A) Selected regions of the CCC1 promoter or mutated regions of the CCC1 promoter sequence were cloned into lacZ reporter constructs, and the constructs were transformed into wild-type cells grown in iron-limited medium. Iron (500 μM FeSO4) was added to the medium for 2 h, cells were harvested, β-galactosidase activity was determined, and activity was normalized for protein (yellow bars with associated numbers). The data are presented as the change in β-galactosidase activity. The green ovals represent consensus YAP binding sites, and the × indicates the site of mutations. The 46-bp region is highlighted with a red bracket. (B) Wild-type (WT) and YAP deletion strains in the BY4741 haploid deletion collection were spotted in serial dilutions on medium containing high concentrations of iron. The cells were grown for 2 days at 30°C. (C) Wild-type and yap5Δ cells (haploid W303 background) were transformed with a plasmid containing a CCC1-lacZ reporter construct. Cells grown in iron-limited medium were incubated with (black bars) or without (white bars) 500 μM FeSO4 for 2 h, β-galactosidase activity was determined, and activity was normalized for protein.