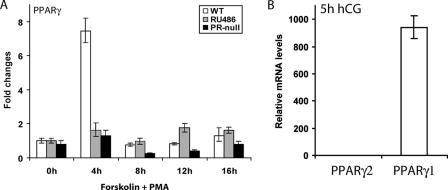
FIG. 3.
Expression of PPARγ in primary mouse granulosa cell cultures. (A) PR-dependent expression. Primary granulosa cells were extracted from ovaries of prepubertal (21 to 23 days old) WT (+/+) and PR-null (−/−) mice primed with PMSG for 48 h. To stimulate LH signaling, these cells were treated with a combination of forskolin (10 μM), an adenylyl cyclase activator that stimulates the protein kinase A pathway, and PMA (10 nM), a diacylglycerol analog that activates the protein kinase C pathway. RU486, a PR antagonist, was added to the WT primary cells along with forskolin and PMA to block P action. (B) Estimation of the relative levels of PPARγ1 and PPARγ2 transcripts in gonadotropin-stimulated granulosa cells. Granulosa cells were extracted from the ovaries of WT mice treated with PMSG for 48 h, followed by hCG for 5 h. Total RNA isolated from these cells was subjected to real-time PCR employing two distinct sets of primers, one specifically detecting PPARγ2 and the other detecting both isoforms. Since PPARγ2 transcripts were virtually undetectable, we infer that the PPARγ mRNAs represent transcripts corresponding to the γ1 isoform. The n-fold induction indicates the gene expression level at 5 h of hCG treatment relative to 0 h of hCG treatment as described in Materials and Methods.