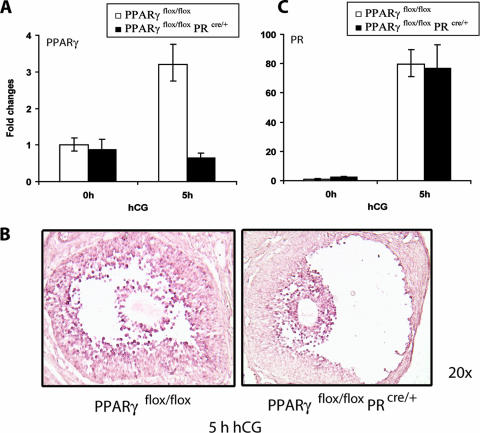
FIG. 4.
PR-Cre-mediated excision of PPARγ in the preovulatory follicles of conditional PPARγ mutant mice. (A) PR-Cre-mediated ablation of the PPARγ floxed gene in the ovary. Cre-mediated excision of the floxed PPARγ gene was assessed by measuring the expression levels of PPARγ mRNA in ovaries of PPARγflox/flox and PPARγKO (PPARγflox/flox PRcre/+) mice following gonadotropin-induced ovulation. Ovaries were collected from PPARγflox/flox and PPARγKO (PPARγflox/flox PRcre/+) mice at 0 h (48 h PMSG) and 5 h after administration of hCG following 48 h of PMSG treatment. Total RNA was extracted and converted to cDNA by reverse transcription. The level of PPARγ expression was analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR using 36B4 as a normalizing control. (B) Cell type-specific loss of PPARγ expression in the ovary. PPARγ mRNA expression was examined by in situ hybridization in ovaries collected from PPARγflox/flox) and PPARγKO (PPARγflox/flox PRcre/+) mice at 5 h hCG following 48 h of PMSG treatment by using digoxigenin-labeled sense and antisense RNA probes specific for PPARγ. (C) Expression of PR mRNA in PPARγ conditional mutant ovaries. Ovaries were collected from PPARγflox/flox and PPARγflox/flox PRcre/+ mice at 0 and 5 h after administration of hCG following 48 h of PMSG treatment. Total RNA was isolated and converted to cDNA, and the levels of PR mRNA expression were analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR using 36B4 as a normalizing control. Changes were calculated corresponding to the PR mRNA level in 0-h PPARγflox/flox ovaries.