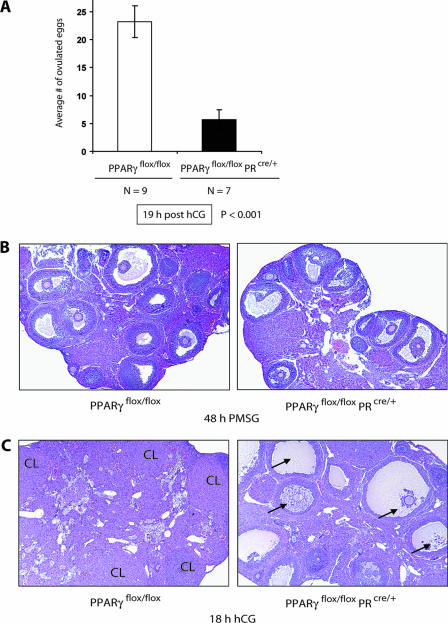
FIG. 5.
Phenotypic effects of PPARγ gene deletion during ovulation. (A) Ovulatory effects of a PPARγ conditional mutation in the preovulatory follicles. Age-matched PPARγflox/flox and PPARγflox/flox PRcre/+ (PPARγ conditional null) mice were superovulated with PMSG for 48 h, followed by hCG for 18 h, and the ovulated eggs were counted. The average ± the standard error of the mean was estimated, and statistical significance was assessed at a critical P value (α) of 0.05. (B) Follicular development in the conditional mutant ovary. The effect of PPARγ deletion on follicle development was assessed by examining the ovarian histology of PPARγflox/flox and PPARγflox/flox PRcre/+ mice following stimulation of follicular development by treatment with PMSG for 48 h. The ovaries were fixed in 10% formalin. Paraffin-embedded sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and examined by light microscopy (magnification, ×5). (C) Impaired rupture of preovulatory follicles deficient in PPARγ. The ovaries of PPARγflox/flox and PPARγflox/flox PRcre/+ mice were collected at 18 h after administration of hCG following the superovulation experiment as described for panel A and examined histologically to determine the state of follicular rupture. The arrows (right) refer to unruptured preovulatory follicles. Although the oocyte was not visible in some of the unruptured follicles, its presence was confirmed in adjacent paraffin sections obtained from the same tissue. A small number of corpora lutea were also seen in the mutant ovaries.