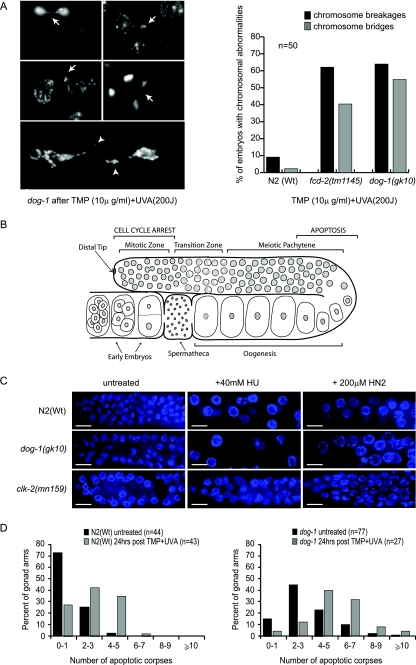
FIG. 3.
Chromosomal aberrations are present, and the DNA damage checkpoint is active, in dog-1 mutants after cross-linking treatment. (A) Representative chromatin bridges (arrows) and breaks (arrowheads) observed in the germ lines of dog-1 mutants following treatment with TMP (10 μg/ml) and UVA (200 J). Quantification of chromosome breakages and bridges in N2(Wt), fcd-2(ok1145), and dog-1(gk10) animals following treatment with TMP-UVA showed similar numbers of breaks and bridges in fcd-2 and dog-1 mutants. (B) Schematic of the C. elegans germ line. Nuclei in the mitotic zone serve as the stem cell compartment of the germ line and undergo cell cycle arrest following DNA damage. Nuclei move through the transition zone, where they take on a characteristic crescent shape as they begin the early stages of meiosis I. Meiosis progresses through pachytene, diplotene, and diakinesis, and completes once the oocyte has been fertilized. Cells in late pachytene/early diplotene undergo apoptosis in response to physiological cues or DNA damage. Early embryos are visible prior to ovulation. (C) Germ line mitotic zone nuclei of N2(Wt), dog-1, and clk-2 mutants stained with DAPI. Enlarged arrested nuclei were observed in the germ line mitotic zones of N2(Wt) and dog-1, but not in clk-2 mutants, following treatment with 40 mM HU or 200 μM nitrogen mustard (HN2). (D) Numbers of SYTO12-stained corpses in N2(Wt) and dog-1 animals with no treatment and 24 h after DNA cross-linking with TMP-UVA treatment (n, number of animals scored for apoptosis).