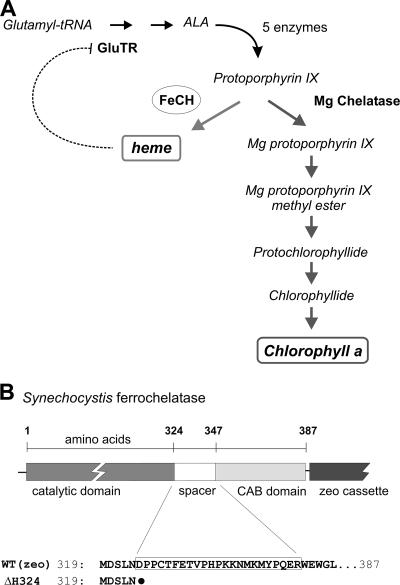
FIG. 1.
(A) The tetrapyrrole biosynthetic pathway in cyanobacteria. FeCH (circled) lies at the branch point between heme and Chl biosynthesis, sharing the same substrate Proto with the magnesium chelatase. The positions of the Chl precursors relevant for this study are also shown. This model of pathway regulation (reviewed in references 1 and 37) proposes that activity of the glutamyl-tRNA reductase (GluTR) at the beginning of the pathway is inhibited by heme (dotted line), which in turn controls synthesis of the ALA and ultimately the total flux through the pathway. (B) Schematic presentation of the Synechocystis FeCH with catalytic and C-terminal CAB domains connected by a spacer. The position of the zeocin (zeo) resistance cassette is also indicated. Amino acid alignment of the FeCH C terminus shows the FeCH truncation in the ΔH324 strain; the black dot indicates a stop codon.