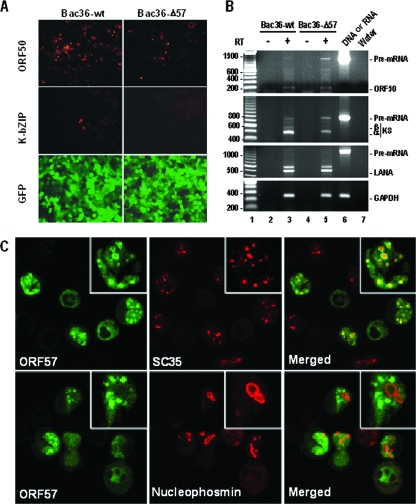
FIG. 1.
KSHV ORF57 regulates the expression of viral intron-containing genes and distributes in nuclear splicing speckles in KSHV-infected B cells. (A) KSHV ORF57 is important for production of viral ORF50 and K-bZIP proteins. HEK-293 cells stably transfected with Bac36-wt or Bac36-Δ57 DNA were induced by sodium butyrate for lytic infection and stained with anti-ORF50 or anti-K8 (K-bZIP) antibody. GFP expression from Bac36-wt and Bac36-Δ57 genomes in the HEK-293 cells was imaged directly from the fixed cells. (B) Accumulation of ORF50 and K8 pre-mRNAs in butyrate-induced stable Bac36-Δ57 cells. Total RNA extracted 24 h after butyrate induction from HEK-293 cells stably transfected with Bac36-wt or Bac36-Δ57 was analyzed by RT-PCR for the expression of KSHV ORF50, K8, and LANA RNAs using a pair of gene-specific exon primers (Table 1). The primer pair oKY30 and oKY46 was used for LANA detection. Cellular glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA served as the RNA loading control. Lane 6 indicates that Bac36 DNA in ORF50, K8, and LANA detection served as controls in each assay. (C) Distribution of KSHV ORF57 in nuclear speckles in KSHV-infected JSC-1 cells. Butyrate-activated JSC-1 cells were stained with rabbit anti-ORF57, mouse monoclonal anti-SC35, or antinucleophosmin and were then imaged by using fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (green) or tetramethyl rhodamine isothiocyanate-labeled anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (red). Insets show enlarged representative cells.