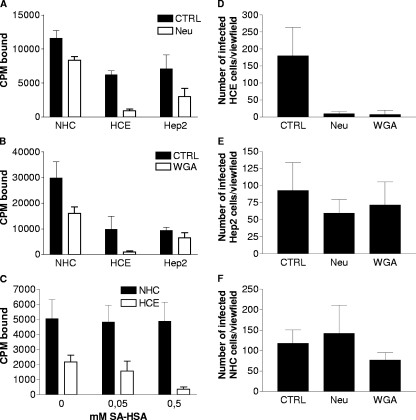
FIG. 4.
Cell surface sialic acid is required for efficient binding of CVA24v to and infection of human ocular cells. Binding was carried out as described for Fig. 1. (A) Cells (2 × 105) in suspension were pretreated with or without neuraminidase from V. cholerae prior to incubation of the cells with 5,000 35S-labeled CVA24v virions per cell. (B) Cells (2 × 105) in suspension were preincubated with or without WGA prior to incubation with 5,000 35S-labeled CVA24v virions per cell. (C) 35S-labeled CVA24v virions (5,000 virions/cell) were preincubated with or without 13-valent sialic acid linked to albumin (SA-HSA) prior to virion-cell incubation (2 × 105 cells/sample; concentrations of SA-HSA are in mM and with respect to sialic acid monosacharrides). (D to F) Adherent HCE (D), NHC (E), or Hep2 (F) epithelial human cell lines were pretreated with or without neuraminidase from V. cholerae or preincubated with or without WGA prior to incubation with virus (500 virions per cell) at 4°C. After one hour, the cells were washed to remove unbound virions and then incubated for 16 to 18 h at 37°C. They were fixed with methanol, stained as described in Materials and Methods, and quantified in a fluorescence microscope. The results are presented as means ± standard deviations of duplicate samples from at least three independent experiments. CPM, counts per minute.