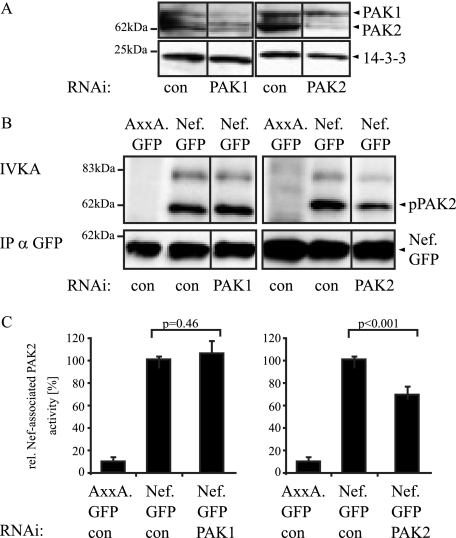
FIG. 3.
Effect of RNAi knockdown of PAK1 and PAK2 on Nef-associated PAK activity. (A) JTag T lymphocytes were transfected with small interfering RNA oligonucleotides specific for PAK1 or PAK2 or a nonspecific control oligonucleotide (con) and analyzed by Western blotting for PAK1 and PAK2 expression levels at 48 and 72 h posttransfection, respectively. 14-3-3 was used as a loading control. (B) Analysis of Nef-associated PAK activity following PAK1 and PAK2 knockdown. JTag T lymphocytes were transfected with small interfering RNA oligonucleotides specific for PAK1 or PAK2 or the control oligonucleotide together with an expression plasmid for Nef.GFP or the AxxA.GFP mutant, and an IVKA following anti-GFP immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed at 48 (PAK1) or 72 (PAK2) hours posttransfection. Nef-associated PAK activity is revealed by the phosphorylated 62-kDa band (IVKA, pPAK2). (C) Quantification of the Nef-associated PAK activity. Intensities of autophosphorylated PAK2 signals were quantified relative to the amounts of immunoisolated Nef.GFP. The relative associated PAK activity for Nef.GFP in the presence of a control oligonucleotide was arbitrarily set to 100%. Data are means ± standard deviations from at least five independent experiments. Statistical significance is indicated by the P values derived from Student's t test analysis. wt, wild type.