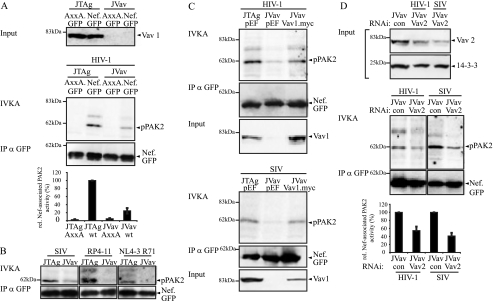
FIG. 5.
Vav1 deficiency reduces Nef-PAK2 association in T lymphocytes. (A) IVKA for Nef-associated PAK2 activity in JTag and Vav1-deficient JVav T lymphocytes. IVKA reactions were performed for Nef from HIV-1 SF2. Vav1 expression levels are shown in the upper panels; the middle panel depicts PAK2 autophosphorylation levels and amounts of immunoisolated Nef. The graphs present relative levels of Nef-associated PAK2 activity, with values for wild-type (wt) Nef in JTag cells set to 100%. Data are means ± standard errors of the means from three independent experiments. IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) IVKA reaction and Western blot analysis for immunoisolated Nef from SIVmac239, HIV-1 RP4-11, and HIV-1 NL4-3. T71R, HIV-1 RP4-11, and SIVmac239. (C) Rescue of HIV-1 SF2 Nef-associated PAK2 activity in JVav cells by Vav1 overexpression. Shown are the IVKA reaction, amounts of immunoisolated Nef, and Vav1 expression levels. (D) Residual Nef-associated PAK2 activity in JVav cells is sensitive to RNAi against Vav2. JVav cells were treated with the indicated RNAi oligonucleotides, and knockdown efficiency was evaluated by Western blotting (upper panel). From the same lysates, an IVKA was performed (middle panel). The bottom panel presents the quantification of Nef-associated PAK2 activity, with values for wt Nef in JVav cells treated with a control oligonucleotide set to 100%. Data are means ± standard errors of the means from three independent experiments.