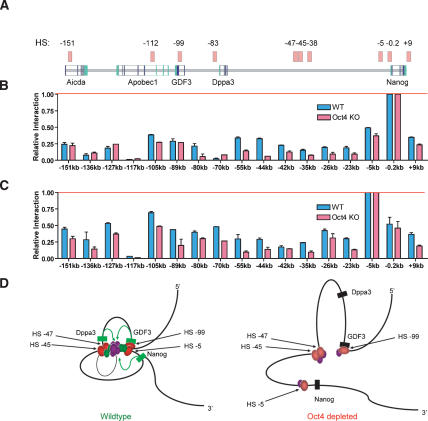
Figure 4.
Long-range chromosomal contacts connect HSs throughout the Nanog locus. (A) A schematic of the Nanog locus, with HS indicated by light-red boxes. The region of chromosomal contact, relative to the Nanog start site, is shown below each graph. The red bar shows normalization against a nonchimeric amplification product at the specified region of analysis. HS up to 150 kb away make contact with the Nanog proximal promoter. (B,C) Chromosome conformation at the Nanog proximal promoter and −5-kb HS. Wild-type ES cells are indicated in blue and 72-h Oct4-depleted cells are in red. Higher-order structure is lost throughout the locus following Oct4 depletion. (D) A two-dimensional rendering of chromatin looping in three-dimensional space between distant regulatory elements (red ovals) and Nanog locus genes (green and black rectangles indicate active and repressed states, respectively). The model depicts DNA-bound factors within the proximal promoters of GDF3, Dppa3, and Nanog initiating contact (green arrows) with an active transcriptional node formed by RNA polymerase II (large purple oval); accessory DNA-binding or bridging transcription factors p300, ZFP281, Nac1, and CTCF (smaller purple ovals); and essential DNA-bound transcription factors Oct4 and Nanog (green ovals).