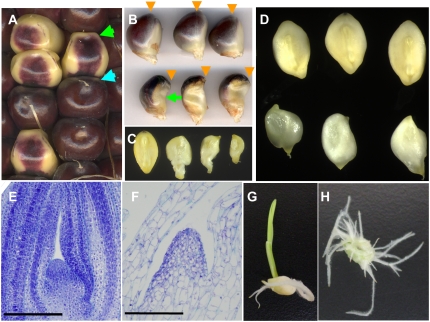
Figure 1.
Phenotypes of the wpk1 mutant seeds and seedling. A, Ear segregating wpk1-umu1. Wild-type and wpk1 mutant seeds are indicated by blue and green arrows, respectively. B, Lateral views of mature seeds of wild type (top) and wpk1 (bottom) are shown. The positions of silk attachment are indicated by orange arrows. The green arrow highlights deficiency of anthocyanin accumulation in the germinal region of wpk1. C, A wild-type embryo (left) and three wpk1 embryos are shown. The embryos were excised from the seeds shown in B. D, Three developing embryos for wild type (top) and wpk1 (bottom) are shown. The embryos were excised from the seeds at 20 DAP. E and F, Embryonic SAMs of wild-type (E) and wpk1 (F) embryos at 16 DAP. Scale bars = 200 μm. The multiple embryos were sectioned and examined through histological analysis to confirm the altered development of SAM of the wpk1 mutant embryos. G and H, Seedlings from rescued wild-type control and wpk1 mutant embryos.