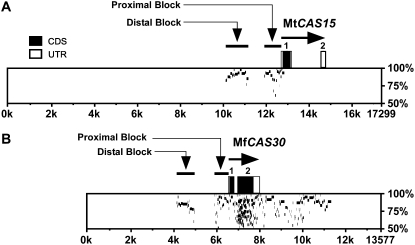
Figure 4.
PIPs between the M. truncatula and M. falcata CAS15 and CAS30/31 genomic regions. A, PIPs between 17,299 bp of the M. truncatula CAS15 genomic region (horizontal axis) and the 7,779 bp M. falcata genomic clone λ7H-15-2 (vertical axis). (The MfCAS15 genomic clone λ7H-15-2 terminates at amino acid residue Q27.) B, PIPs between the 13,577 bp of M. falcata CAS30 genomic clone λV2-17 (horizontal axis) and the 14,288 bp M. truncatula λJ2-17-2 genomic clone (vertical axis). The MtCAS31 genomic clone λJ2-17-2 terminates at −1,728 within the distal upstream identity block. Exons 1 and 2 are shown as boxes; black boxes are protein CDSs, gray boxes are untranslated regions (UTR). The percent identity between the genomic regions from 50% and 100% is presented on the vertical axis. The multiple horizontal bars at the same position along the x axis under Exon 2 in CAS30 are a result of the low complexity and multiple repeating unit structural composition of dehydrins.