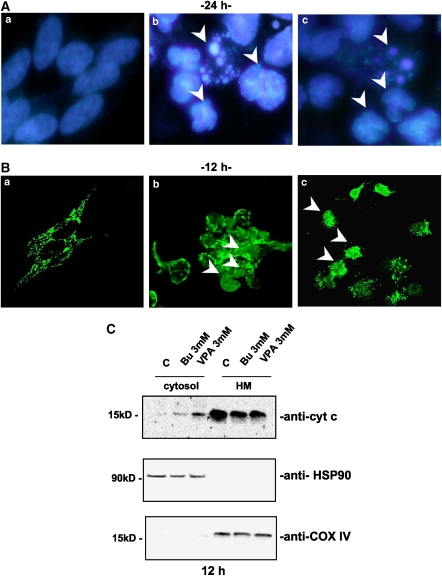
Figure 2.
HDAC inhibitors induced a typical apoptotic death. (A) Nuclear fragmentation of neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y) was assessed by fluorescent DNA staining. DRAQ5 nuclear dye showed the presence of fragmented, indented or condensed (arrows) nuclei only with the higher (b) butyrate or (c) VPA concentration (3 mM) used ((a) untreated control cells after 24 h in culture). (B) Confocal microscopy of cytochrome c (cyt c) mitochondrial de-localization (arrows) in SH-SY5Y following 12 h treatment with 3 mM (b) butyrate (Bu) or (c) VPA treatment and (a) control cells. (C) Western blot analysis of cytochrome c localization following subcellular fractionation (cytosol: soluble cytosolic fraction, 25 μg per lane; HM: heavy membrane fraction, 10 μg per lane) of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells treated with Bu or VPA (12 h incubation). Heat-shock protein-90 (HSP-90) and cytochrome oxidase subunit IV (COX-IV) were evaluated as housekeeping proteins for cytosolic (HSP-90) or mitochondrial (COX-IV) fractions. Experiments on SK-N-BE cells gave similar results.