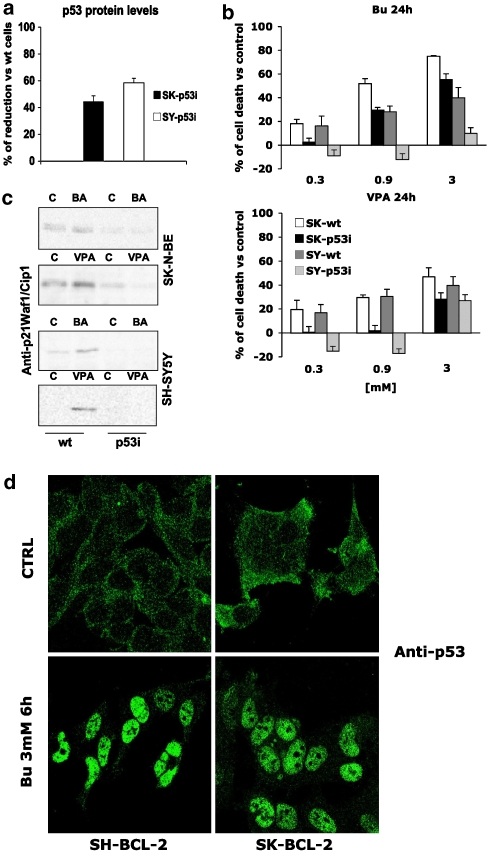
Figure 7.
p53 dependence of HDAC inhibitor-induced effects. (a) Densitometric analysis of p53 interference (p53i) vs SH-SY5Y and SK-N-BE parental cell lines. Absorbance values of western blot p53-reactive bands from p53i cells were corrected for the β-actin values (internal standard) compared with the values obtained from parental cell lines and expressed as % of reduction. (b) Cell death of wild-type (wt) and p53i SH-SY5Y and SK-N-BE cells treated for 24 h with different butyrate or VPA concentrations. Results (expressed as % cell death vs untreated controls) represent the means±s.e. of three different experiments performed in quadruplicate. (c) Western blot analysis of p21/Waf1/Cip1 expression in wt and p53i SH-SY5Y and SK-N-BE cells following HDAC inhibitor treatment (0.9 mM, 8 h). (d) Bcl-2 overexpression did not affect HDAC inhibitor-induced p53 nuclear translocation. Parental SH-SY5Y and SK-N-BE cell lines or their Bcl-2 overexpressing derivatives were treated with butyrate (0.9 mM) for 6 h and p53 subcellular localization was studied by confocal microscopy with an anti-p53-specific antibody. Similar results were obtained after VPA treatment (not shown).