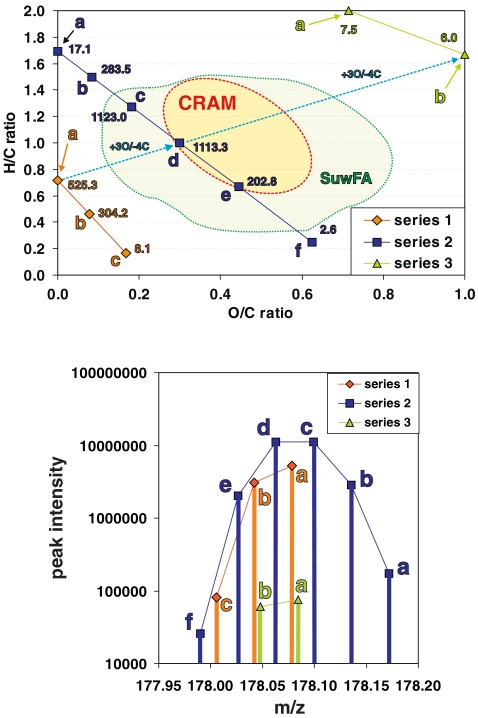
Fig. 11.
The relationship between the FTICR mass spectral intensity and the number of feasible isomers in complex materials. The distribution of (chemically relevant) C,H,O-isomer counts within the C,H,O-compositional space is visualized here in a van Krevelen diagram (left) for the eleven feasible molecular compositions CnHmOq that have an IUPAC nominal mass of 178 Da (see the main text). These molecules are arranged into three series (series 1a–1c with three members; series 2a–2f with six members; series 3a–3b with two members) of isobaric molecules, which are related by a formal exchange of CH4 against oxygen. For any molecular composition, the number of chemically relevant isomers is given in units of 104. Carboxyl-rich alicyclic molecules (CRAM), which represent a complex mixture of molecules with near-absent olefinic and aromatic unsaturation, have recently been identified in marine organic matter [18], and they occupy an area of C,H,O-compositional space for which the largest number of feasible C,H,O-isomers is expected (see the main text), suggesting that the actual number of different molecules in the mass spectra of CRAM for any given mass may correlate with mass spectral intensity patterns. The availability of aromatic moieties in Suwannee river fulvic acid (SuwFA) also allows chemically relevant structures at lower H/C ratios (see the main text). The green circumfenced area denotes the van Krevelen compositional space of SuwFA, as provided in Fig. 9 (note that the SuwFA here represents consolidated positive and negative ion APCI+APPI+ESI FTICR mass spectra, as opposed to the negative ion ESI FTICR mass spectra given in the case of CRAM; see the main text). The panel on the right shows the CnHmOq isomers computed for an IUPAC nominal mass of 178 Da in an intensity versus mass display (analogous to a mass spectrum), denoted according to series 1–3 (see the main text). This pattern resembles the clusters of peaks observed in good-quality FT mass spectra of NOM (see Fig. 6, bottom panels, and Fig. 8), suggesting that the intensities of the C,H,O-derived mass spectral peaks of NOM follow the number of chemically relevant C,H,O-isomers computed