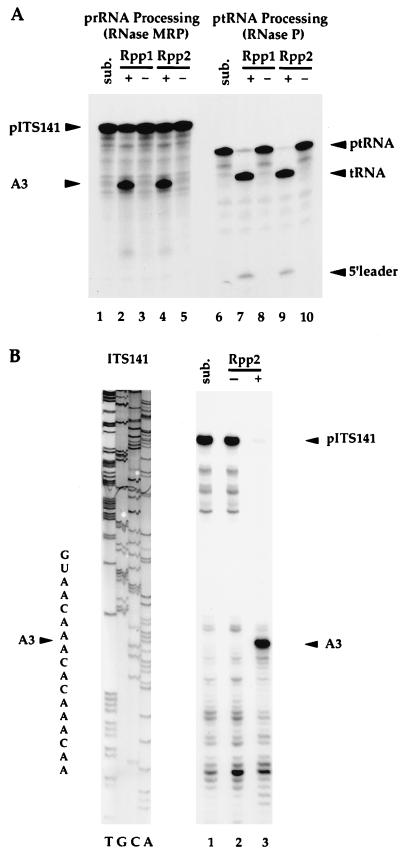
Figure 3.
RNase P and RNase MRP coprecipitate with Rpp2 and accurately cleave both ptRNA and prRNA substrates. (A) Immunoprecipitates derived from wild-type cells (−; VS211B) and individually epitope-tagged Rpp1 (+; VS162B, see ref. 14) and Rpp2 (+; VS202A) cells were resuspended with internally labeled prRNA (ITS141, see ref. 14) (lanes 1–5) and ptRNASer (lanes 6–10) and incubated for 1 hr at 37°C (see Materials and Methods). Sub. (lane 1) is precursor rRNA, ITS141, and sub. (lane 6) is precursor tRNASer. (B) The ITS141 RNA was transcribed in vitro and was incubated with immunoprecipitates derived from wild-type cells (−; VS211B, lane 2) and FLAGHISRPP2 cells (+; VS202A, lane 3). Sub. (lane 1) is ITS141. Accurate cleavage of the prRNA substrate at the A3 cleavage site was determined by primer extension analysis of the cleaved products. A 5′ end-labeled oligonucleotide (Oligo 6, which hybridized 40 nt 3′ to the A3 cleavage site; see ref. 14) was used in a primer extension reaction. Primer extension products were resolved on an 8% polyacrylamide/7 M urea gel. ITS141 was sequenced with the same oligonucleotide as was used for the primer extension reaction.