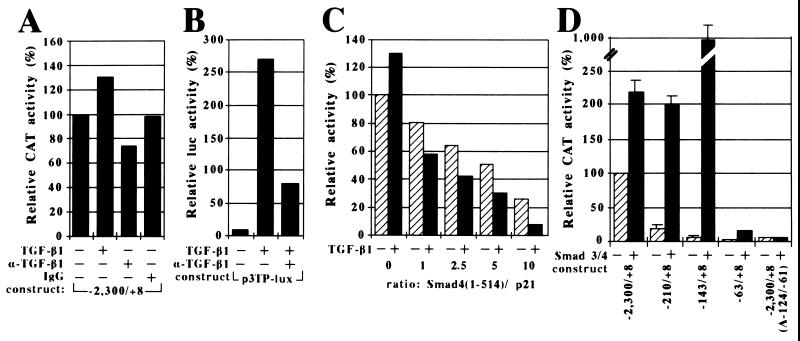
Figure 2.
Regulation of the p21 promoter by TGF-β1 and Smad proteins. (A and B) Effect of TGF-β1 on p21 and 3TP promoter activity. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with the −2,300/+8 p21 (A) or the p3TP-lux (B) reporter constructs alone (−) or in the presence (+) of TGF-β1 with (+) or without (−) a neutralizing anti-TGF-β1 antibody or a sheep IgG. Relative CAT (A) or luciferase (B) activity is reported. The activity of the −2,300/+8 p21 promoter in the absence of TGF-β1 and antibodies was set arbitrarily to 100%. (C) Dose-dependent repression of the −2,300/+8 p21 promoter activity by Smad4(1–514). HepG2 cells were cotransfected with the −2,300/+8 p21 reporter plasmid and increasing amounts of Smad4(1–514) in the absence (−, striped bars) or presence (+, solid bars) of TGF-β1. The ratio of Smad4(1–514) to −2,300/+8 p21 reporter plasmid input is indicated. (D) Mapping of the p21 promoter region that mediates transactivation by Smad3/4. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with the indicated p21 reporter plasmids without (−, striped bars) or with (+, solid bars) expression vectors for Smad3 and Smad4. The activity of the −2,300/+8 p21 promoter in the absence of Smads was set arbitrarily to 100%.